
Germany
Partner in global health
This content was last updated on 25 March 2025.
Shaping global health
Germany stands as a global leader in public health, showcasing its commitment through robust health strategies, policies, and contributing with expertise and funding to the World Health Organization.
The partnership between WHO and Germany focuses on strengthening global health security, combating antimicrobial resistance and advancing universal health coverage, with the shared goal of building resilient health systems that save lives and protect the most vulnerable. Germany hosts the WHO Hub for Pandemic and Epidemic Intelligence in Berlin, a major initiative to enhance global preparedness for future health threats.
Germany's global health influence extends to global platforms like the G7 and G20, where it consistently prioritizes health. Notably, Germany called on WHO to lead the creation of the Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-being for All, to accelerate progress on the health-related Sustainable Development Goals.
At the 2024 World Health Summit in Berlin, Federal Chancellor Scholz announced Germany's commitment to WHO of nearly US$ 400 million over the next four years, including more than US$ 260 million in new voluntary funding. In his address, the Chancellor said: "The WHO's work benefits us all. What it needs for this work is sustainable financing that gives it the certainty to plan ahead and the flexibility to react."
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Germany played a pivotal role in the global response, steering the G20 finance ministers' economic action plan to address the crisis and actively supporting the ACT-Accelerator, an alliance focused on the equitable distribution of vaccines, tests, and treatments.

Dr Catharina Boehme, Chancellor Olaf Scholz, Dr Tedros at the World Health Summit 2024 in Berlin.
Germany supports WHO's work to advance universal health coverage
Germany contributes to the Universal Health Coverage Partnership, which is one of WHO's largest initiatives for international cooperation for universal health coverage and primary health care, helping more than 120 countries to strengthen their health systems.
Through the UHC-Partnership, more than 140 health policy advisers deployed in WHO country offices provide day-to-day support to countries on health systems, including governance, financing, health workforce, access to medicines, packages of services and health information systems, according to national priorities.
Germany's contribution helped WHO respond to the evolving priorities and rapidly changing national contexts during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Partnership is also working to ensure that the investments made throughout the COVID-19 response will result in health system reforms that improve both health security and progress towards universal health coverage.
Global Action Plan for healthy lives and well-being for all
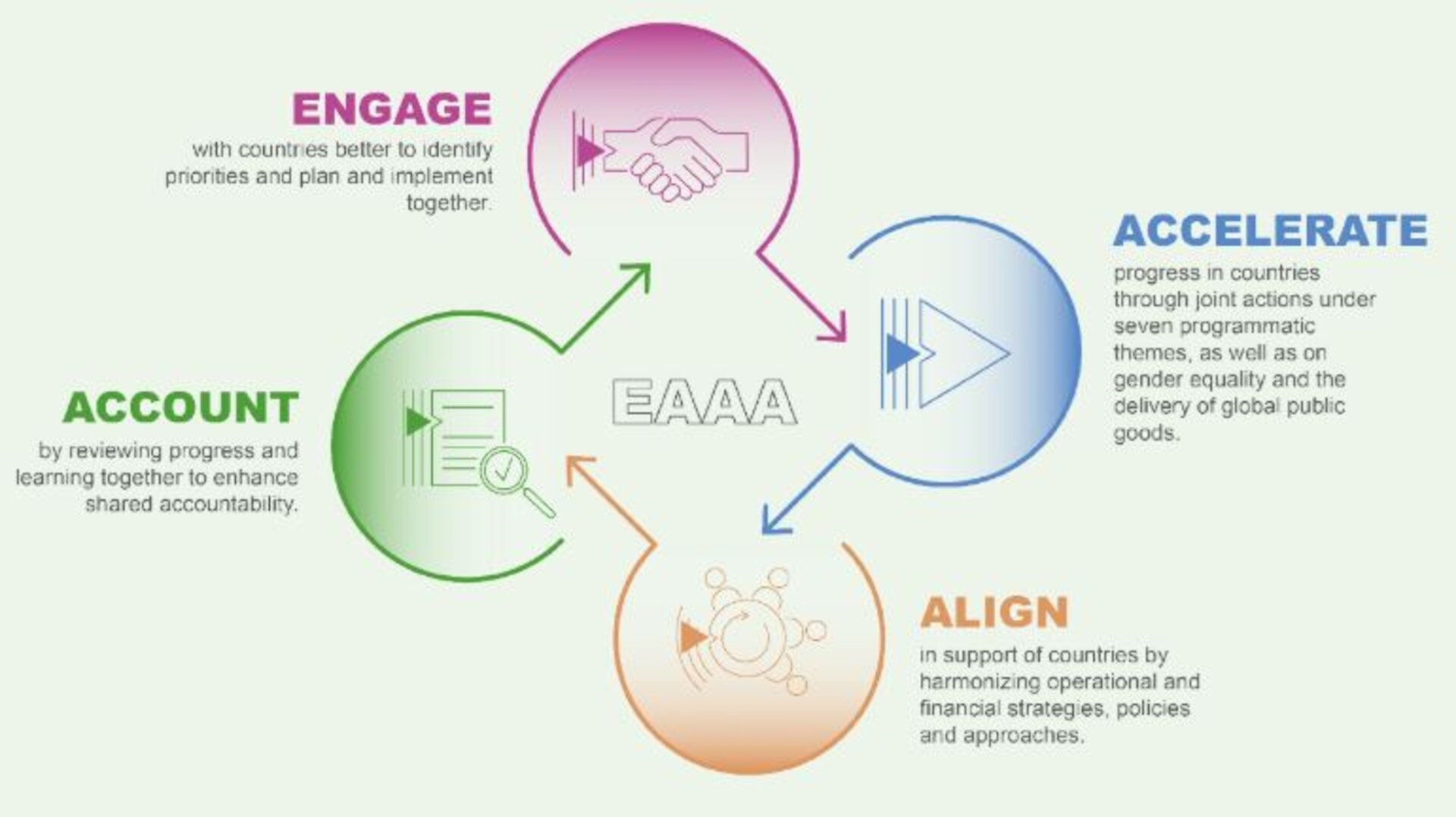
Global Action Plan for healthy lives and well-being for all, graphic from SDG3 GAP brochure: Multilateral agencies commit to Engage, Accelerate, Align, Account (EAAA)
Germany supports WHO’s core function of providing global leadership on health, engaging in partnerships where joint action is needed. Germany was instrumental for putting the Global Action Plan to accelerate progress on the health-related Sustainable Development Goals on the global agenda. The Global Action Plan and strengthened partnerships constituted a crucial asset at a time when countries are striving to protect health gains and build back better from the COVID-19 pandemic with more resilient health systems centred around primary health care, re-doubling efforts to achieve health and well-being for all.
Combating antimicrobial resistance
Since its G20 presidency in 2017, Germany has continuously recognized the global threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and has been a strong supporter and a steadfast, critical WHO partner for addressing AMR globally. In addition to providing substantial financial and institutional support, as well as a Junior Professional Officer for AMR in recent years, Germany nurtures the AMR technical partnership WHO via the Robert Koch Institute — a WHO Collaborating Centre for AMR, consumption and health-care associated infections.
Germany also supports the Quadripartite Joint Secretariat (QJS), which is hosted by WHO and made up of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN (FAO), the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), and the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). Germany helped QJS to foster a One Health multisectoral approach to AMR at global, regional, and country level through the development of a Strategic Framework for Collaboration on AMR and its roll-out in countries. Germany also convened the first "Global Joint Summit of Human and Veterinary Medicines Regulatory Authorities"; has provided technical support and guidance on integrated surveillance and other One Health approaches to AMR in low- and middle-income countries; and contributed to the AMR Multi-Partner Trust Fund.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative
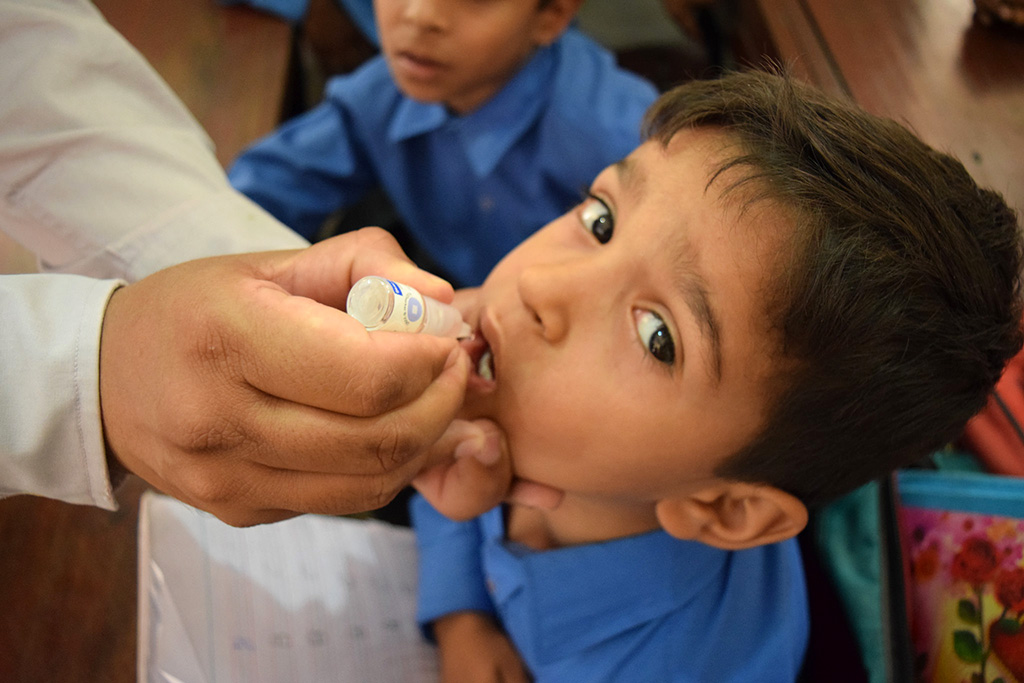
Germany is a long-time supporter of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) with contributions totaling more than US$ 898 million. Fostering global commitment to polio eradication during its G7 and G20 presidencies, Germany garnered international recognition at the highest levels.
At the 2019 World Health Summit, Germany called for continued universal commitment to finish the job. In Germany’s 2020 Strategy Paper Shaping Global Health, Taking Joint Action, Embracing Responsibility, polio eradication forms part of its commitment to global public health and global health security. On the margins of the 2022 World Health Summit, Germany, together with partners, co-hosted a global polio eradication pledging moment, giving the international development community the opportunity to recommit to the global polio eradication effort.
During the World Health Summit in 2024, Minister Svenja Schulze, Federal Minister for Economic Cooperation and Development, announced her new role as GPEI Gender Champion, recognizing the essential role of women in global immunization programs.
WHO collaborating centres in Germany
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Occupational Health
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Sexual and Reproductive Health
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Air Quality Management & Air Pollution Control
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Research in Male Reproduction
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Research on Drinking Water Hygiene
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Health Promoting Water Management and Risk Communication
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Tobacco Control
- WHO Collaborating Centre for the Family of International Classifications
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Quality Assurance of Blood Products and in vitro Diagnostic Devices
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Radiation Emergency Medical Preparedness and Assistance
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation and Health
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Obesity Prevention, Nutrition and Physical Activity
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Physical Activity and Public Health
- WHO Collaborating Centre on quality assurance and empowerment in mental health
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Standardization and Evaluation of Vaccines
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Global Outbreak Alert and Response – GOARN
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Environmental Health Inequities
- WHO Collaborating Centre for viral hepatitis and HIV
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Evidence-based Public Health
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Antimicrobial Resistance, Consumption and Health Care-Associated Infections
- WHO Collaborating Centre on Evidence Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Cancer Therapies
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Health Literacy
- WHO Collaborating Centre Center for Behavioural Research in Global HealTh (BRIGHT)
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Diphtheria
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Research and Training for Health at the Human-Animal-Environment Interface
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Digital Health Education, Research & Development
WHO Collaborating Centres global database.





