
Luxembourg
Partners in global health
General feature in an hospital in Uganda
Making an impact in health development
WHO is proud to partner with Luxembourg, which contributes more than 15% of its official development assistance to the health sector. Since 2009, Luxembourg has provided 1% of its gross national income to development assistance, making it one of the few countries that exceeds the United Nations target of 0.7%.
WHO and Luxembourg work together in key health areas including universal health coverage; reproductive, maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health; health emergencies; polio eradication; and tropical disease research. From 2020 to 2022, Luxembourg is co-chaired the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases, a partnership hosted by WHO.
Luxembourg’s General Development Cooperation Strategy: The Road to 2030 highlights health as a key area for eradicating poverty. Luxembourg has pledged to improve access to safe and affordable health care with stronger domestic health systems, fight the spread of communicable diseases with a focus on HIV/AIDS, and prioritize maternal and child health, including sexual and reproductive health and rights.
The development strategy leverages Luxembourg’s financial expertise to create innovative mechanisms to reach health goals. The country is a charter member of Luxflag and the Agricultural Business Capital Fund, initiatives that promote responsible investment to help reach the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Luxembourg is also one of the eight members of WHO’s Small Countries Initiative, a knowledge-sharing platform in the WHO European region to improve the health and well-being of populations.
Through its participation in WHO’s governance and leadership in innovative initiatives like the Universal Health Coverage Partnership, Luxembourg helps ensure that WHO has the resources to create healthier lives for all people.

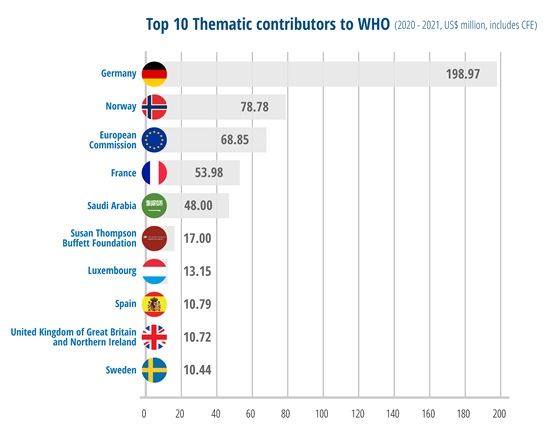
Luxembourg was 7th thematic contributor to WHO in 2020-2021
Luxembourg has traditionally been a strong contributor of flexible funds, providing contributions that are vital for WHO to ensure that critical gaps in funding are filled and allow WHO to act quickly by allocating funds when and where they are needed.
From being amongst the contributors to the Core Voluntary Contributions Account in the biennium 2018-19, Luxembourg became the 7th largest contributor of thematic contributions for 2020-2021.
Note: The amounts represent the revenue received by WHO for the period stated and they might differ from the figures in the WHO Budget Portal, as they represent funds available net of programme support costs.
More about Luxembourg's support to WHO
Top technical areas of funding for the 2020-2021 programme budget include:
- National health policies, strategies and plans
- Reproductive, maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health
- Tropical disease research
- Polio eradication
- Health emergencies
Champions of universal health coverage
Luxembourg is one of the founding members of the Universal Health Coverage Partnership. This innovative partnership supports 115 countries in fostering policy dialogue for strategic planning and health systems governance, developing health financing strategies and supporting their implementation, and enabling effective development cooperation in countries. The achievement of universal health coverage is the overarching goal of Luxembourg's health strategy. Through the Partnership, Luxembourg directly supports six of its partner countries:
Luxembourg supports the UHC Partnership
Ten countries in the African Region were supported by the Partnership to review and update their national health policies and strategic plans in 2021. These include Congo, Eritrea, Gambia, Liberia, Mali, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Seychelles and Zambia.
Rwanda and South Sudan each conducted their respective annual joint health sector reviews and identified future policy directions.
Health insurance reforms and other prepayment mechanisms mainly targeting vulnerable populations were implemented in Chad, Comoros, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Kenya, Madagascar, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, South Africa, Togo, Uganda and Zambia. The Rwanda Community Based Health Insurance Implementation and Sustainability Plan 2021-2030 was developed and validated.
Enabling quick action to save lives
Supporting acute emergency response operations
The WHO Health Emergencies Programme (WHE) works with countries and partners to prepare for, prevent, respond to and recover from all hazards that create health emergencies, including disasters (natural or human-made), disease outbreaks and conflicts.
Funding from Luxembourg has helped to build core capacity to detect disease outbreaks; develop standards to manage high-threat pathogens; respond to health emergencies in crisis countries; and build the capacity in countries to prepare for health emergencies.
Luxembourg has also been a strong supporter to WHO's Contingency Fund for Emergencies (CFE), having made yearly contributions. The CFE allows WHO to respond immediately to disease outbreaks and humanitarian crises. The ability to respond quickly, in as little as 24 hours, can stop a health emergency from spiralling out of control.

WHO Collaborating Centre: Luxembourg Institute of Health
WHO works with the Luxembourg Institute of Health’s Clinical and Applied Virology, Infectious Diseases Research Unit as the WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Measles Infections. It is one of the three WHO regional reference laboratories for measles and rubella in the WHO European Region.
The Luxembourg Institute of Health provides expertise, knowledge sharing and support to national measles and rubella labs in 22 countries in the region, in detecting and characterizing circulating measles and rubella viruses.
Thanks to collaboration with the WHO Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network, Luxembourg enhances disease surveillance capacity and monitoring the efforts toward measles and rubella elimination.

Reproductive , maternal, newborn, child, and adolescent health

There are nearly 1.2 billion adolescents (10- 19 years old) worldwide. In some countries, adolescents make up as much as a quarter of the population. While most adolescent health problems are preventable or treatable, adolescents face multiple barriers in accessing health care and information. WHO is working to support Member States to create transformative outcomes for the world's 1.2 billion adolescents and generations to come, through committing to urgently scale up efforts in service delivery, financing and governance. A new report, Adolescent Health, The Missing Population in Universal Health Coverage, by WHO and partners, outlines how policymakers can act on service delivery, financing and governance.
Eradicating polio
Polio Eradication: PM of Luxembourg Xavier Bettel commits to Global Health at the 2016 Global Citizens Festival
Luxembourg is a long-term supporter and the second-largest per capita donor to polio eradication.Its total contribution to the programme exceeds US$ 20 million. The goal of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative is to complete the eradication and containment of polio viruses, so that no child ever again suffers paralytic poliomyelitis.
At the Global Citizen Festival in 2016, Luxembourg's Prime Minister, Xavier Bettel, voiced his commitment to eradicate polio. Luxembourg pledged to give €500,000 annually until 2023 and provided funds of up to €500,000 for outbreak response to eradicate polio. Luxembourg continues its commitment to polio-eradication efforts. Rotary International presented Prime Minister Bettel, with its prestigious Polio Champion Award in November 2017. Grand Duc Henri of Luxembourg and former Prime Minister Jean-Paul Juncker have also received the award.
Tonight I was honoured to receive the Polio Eradication Champion Award from @Rotary. Luxembourg is committed to support the fight against polio until the end! pic.twitter.com/ovDeXBpelv
— Xavier Bettel (@Xavier_Bettel) November 16, 2017
Clean air for health
The Healthier Kosovo project is financed by the Government of Luxembourg and implemented by WHO, the UN Development Programme and UN Volunteers. It aims to address environmental health issues by strengthening the capacities of national institutions for air pollution and health. Several awareness-raising workshops and trainings have been hosted with the Ministry of Health, most recently using WHO’s AirQ+ software to conduct an environmental health impact assessment.

Luxembourg and WHO on social media
Pleased to sign the MoU with @FranzFayot, 🇱🇺 Minister of the Economy and Minister for Development Cooperation. Thank you 🇱🇺 for your commitment to provide flexible funding to @WHO & help us deliver #HealthForAll, address health emergencies & promote healthier populations. #LuxAid pic.twitter.com/k2aS7mfmXI
— Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus (@DrTedros) June 18, 2020
#Luxembourg and WHO sign new Memorandum of Understanding, committing flexible funds to WHO’s Triple billion targets while addressing gender and women’s empowerment: https://t.co/tYCKJ1k9Ou pic.twitter.com/YqB1RtduuB
— World Health Organization (WHO) (@WHO) June 18, 2020

