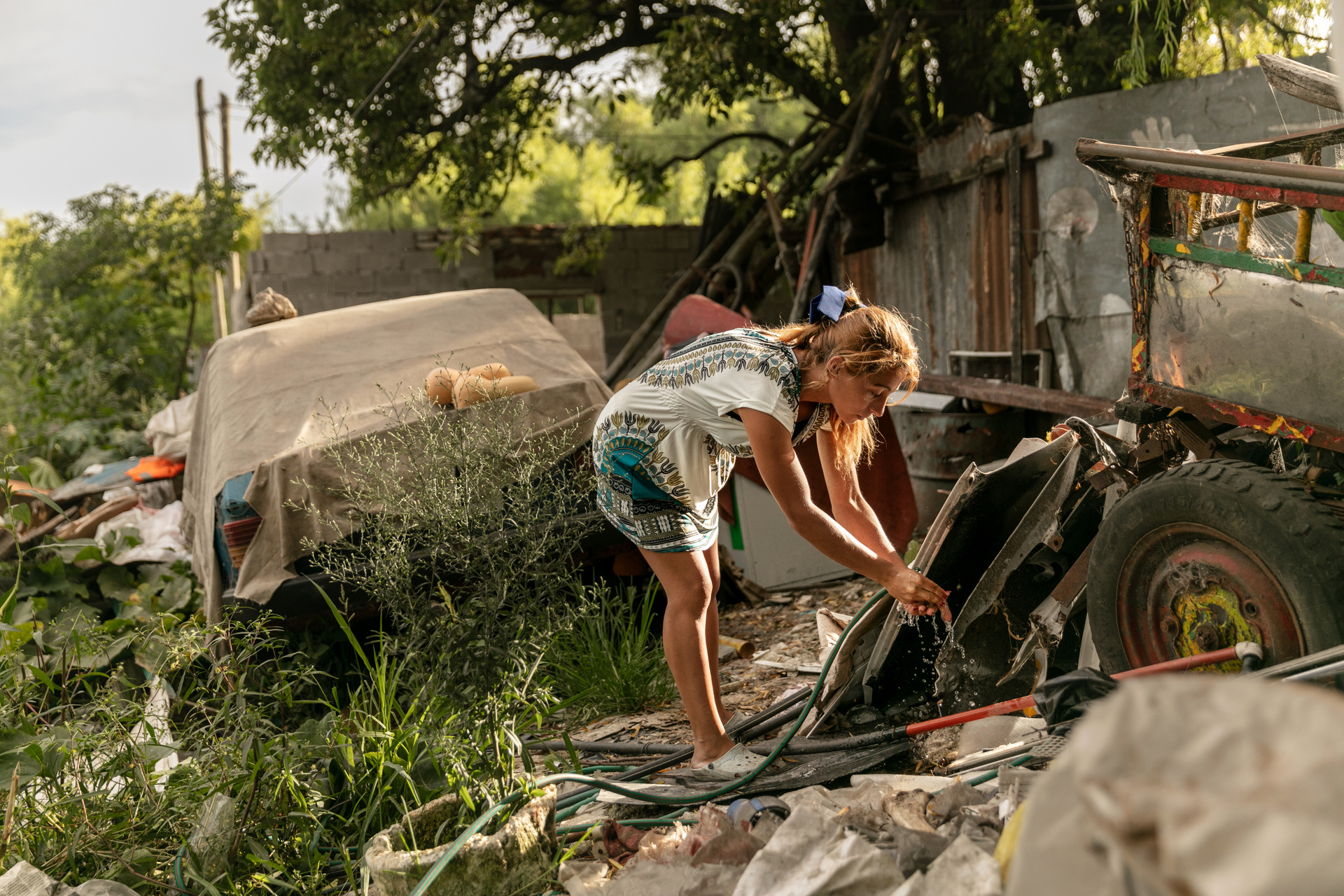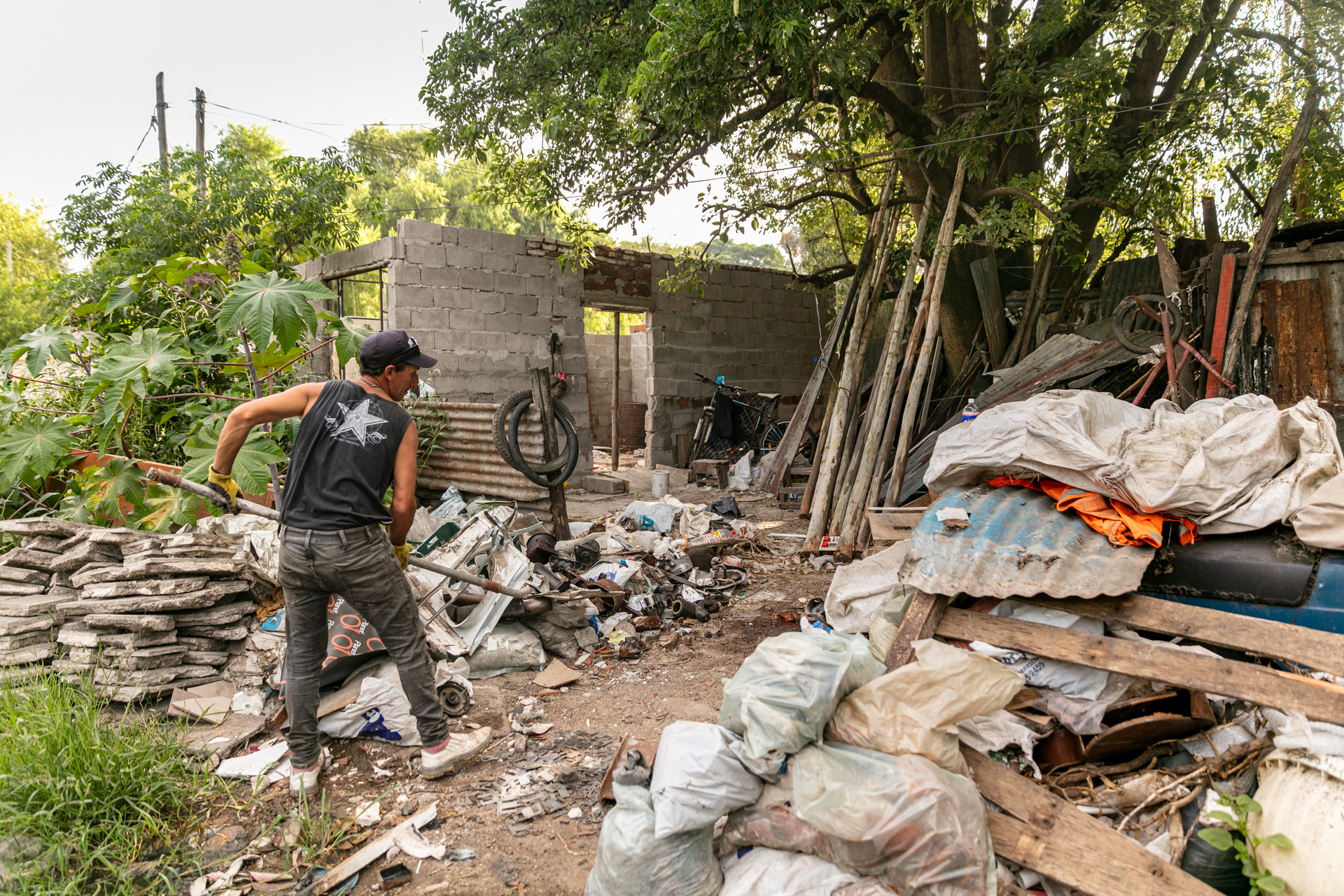Preventing impacts of electronic waste on child health
Electronic and electrical waste (e-waste) is the world’s fastest growing waste stream. According to the Global E-waste Statistics Partnership (GESP), 62 million tonnes of e-waste were produced globally in 2022, but only 22.3% was documented as appropriately disposed of or recycled. E-waste contains valuable resources, such as gold and copper, and recycling these materials has become an important source of income for those working in the informal sector. E-waste also contains highly toxic materials, such as lead and cadmium, which are released into the environment through informal recycling activities.
Children are highly vulnerable to many of these toxic materials and several adverse health effects have been measured in children associated with e-waste recycling. In 2013, WHO launched the WHO Initiative on E-waste and Child Health, setting goals to protect child health from dangerous e-waste recycling. WHO is working on e-waste and child health issues through inter-organizational cooperation, facilitating research, generating evidence and sharing knowledge, developing online courses for health care providers, and contributing to pilot interventions in the African Region and the Region of the Americas. Additionally, WHO and other United Nations agencies are collaborating through an e-waste coalition to address the e-waste challenge at global and local levels.