Management of NCD
people getting their fasting sugar checked for diabetes
Overview
NCD management interventions are essential for achieving the global target of a 25% relative reduction in the risk of premature mortality from NCDs by 2025, and the SDG target of a one-third relative reduction in premature deaths from NCDs by 2030.
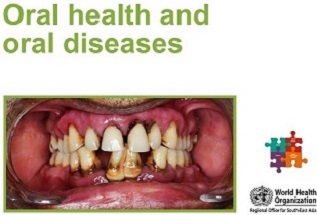
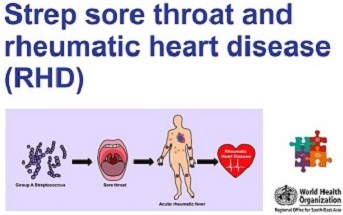
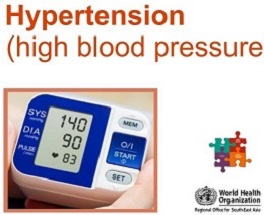
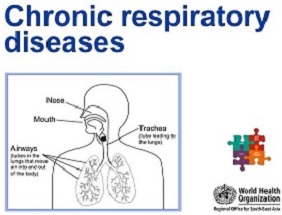
NCD management includes screening, detection and treatment of the diseases, as well as palliative care for those in need.
NCDs require long-term care and repeated interactions with health systems. Three basic elements to improve NCDs response and Universal Health Coverage are; providing the full range of required health services (increasing health systems capacity to respond to NCDs); covering population (addressing inequalities in the NCD burden); and Covering cost (alleviating the economic burden of NCDs).
Integrated NCD service delivery which is accessible, affordable and equitable; implementation of evidence-based management guidelines; availability of essential NCD technologies and medicines in primary health care; sufficient, well trained, and appropriately deployed health workforce; robust patient tracking and health information system for monitoring are essential for NCD management at the primary health care level.
Key facts
WHO Package of Essential NCD interventions will help to improve the coverage of appropriate services for people with NCDs services in primary care settings.
The HEARTS technical package provides a strategic approach to improving cardiovascular health in countries in primary care settings.