Methods for estimating health impacts
Comparative Risk Assessment
The environmental burden of disease quantifies the amount of disease caused by environmental risks.
Disease attributable to the environment can be expressed in deaths and in Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs). The latter measure combines the burden due to death and disability in a single index. Using such an index permits the comparison of the burden due to various environmental risk factors with other risk factors or diseases.
The realization of how much disease and ill health can be attributed to modifiable environmental risks can contribute to identifying opportunities for prevention and should add impetus to global efforts to encourage sound preventive measures through available policies, strategies, interventions, technologies and knowledge.
Additional information required for the rational development of policies by the health sector and activities of other sectors which directly manage or influence the determinants of health includes the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interventions, the availability of resources, and the type of policy environment.
The burden of disease that is caused by an environmental risk can be estimated using a standardized approach –called comparative risk assessment. It is based on the exposure to the risk factor in the population and a measure from a comprehensive analysis of the available evidence of how this exposure translates into health outcomes. The population attributable fraction (PAF) – the proportion of the disease burden that could have been prevented by removing the risk factor or reducing it to a counterfactual level – is calculated from these two inputs (population exposure and exposure-response relationship between exposure and disease). As a last step, the PAF is applied to the total disease burden of a disease, expressed in deaths or DALYs.
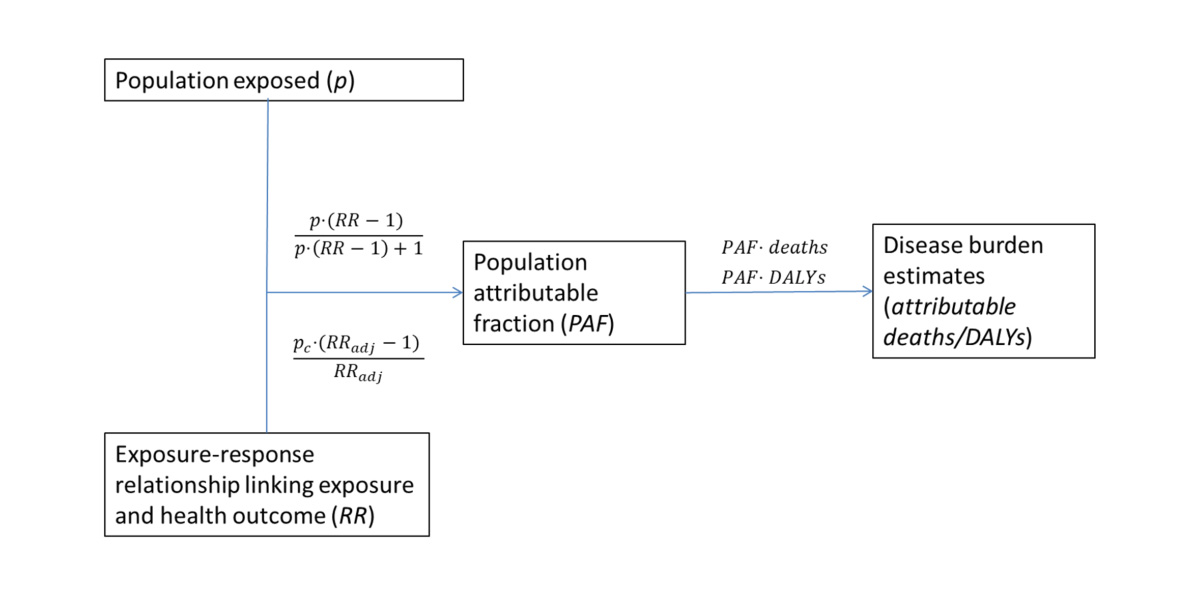
A step-by-step approach of the basic methodology for quantifying environmental health impacts at national and local levels is provided in the Introduction to the EBD Series for assessment at national level.
Selected papers on the method
The methods for quantitative assessment of environmental
health impacts and major results have been documented in various papers.
