Mass Casualty Management in Emergency Units
Overview
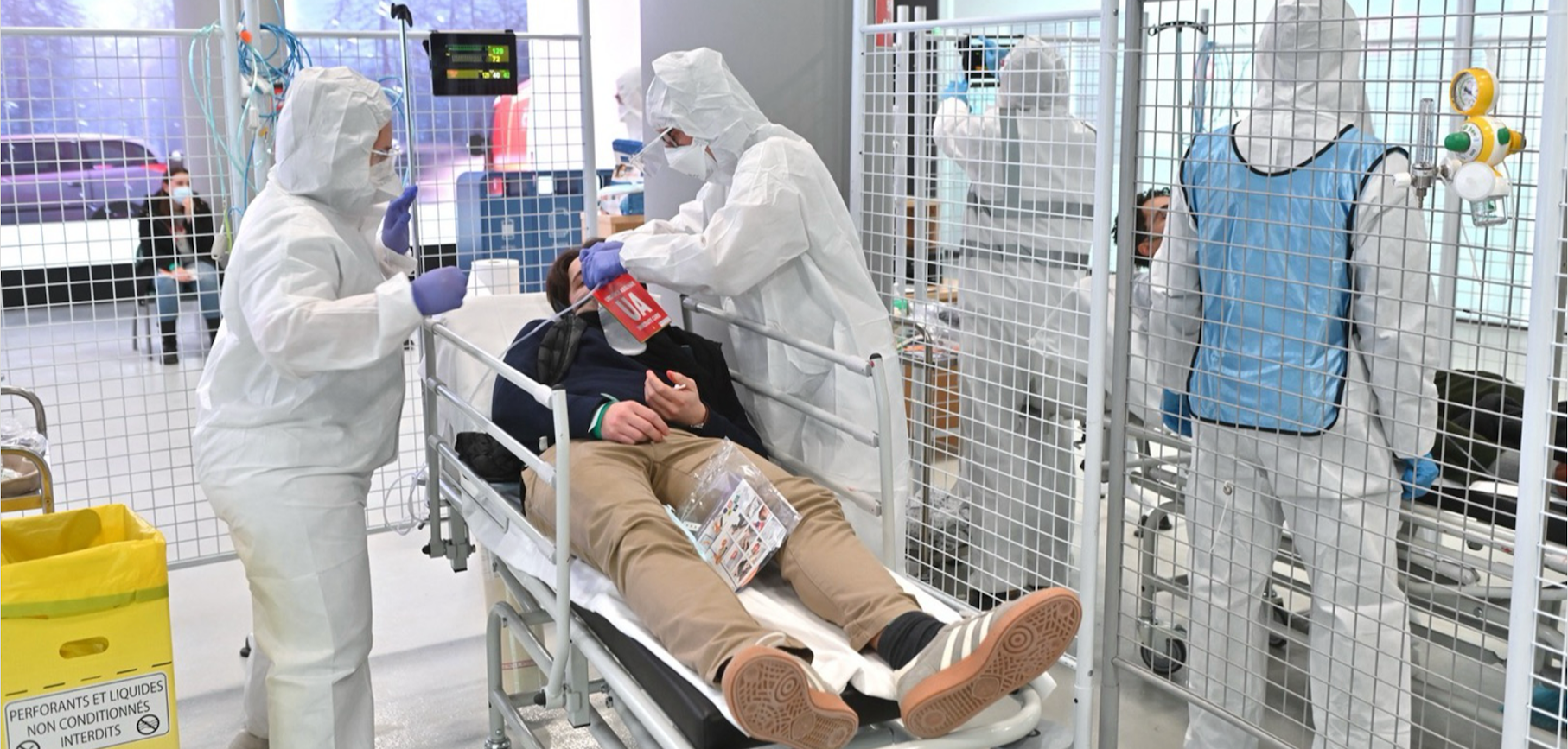
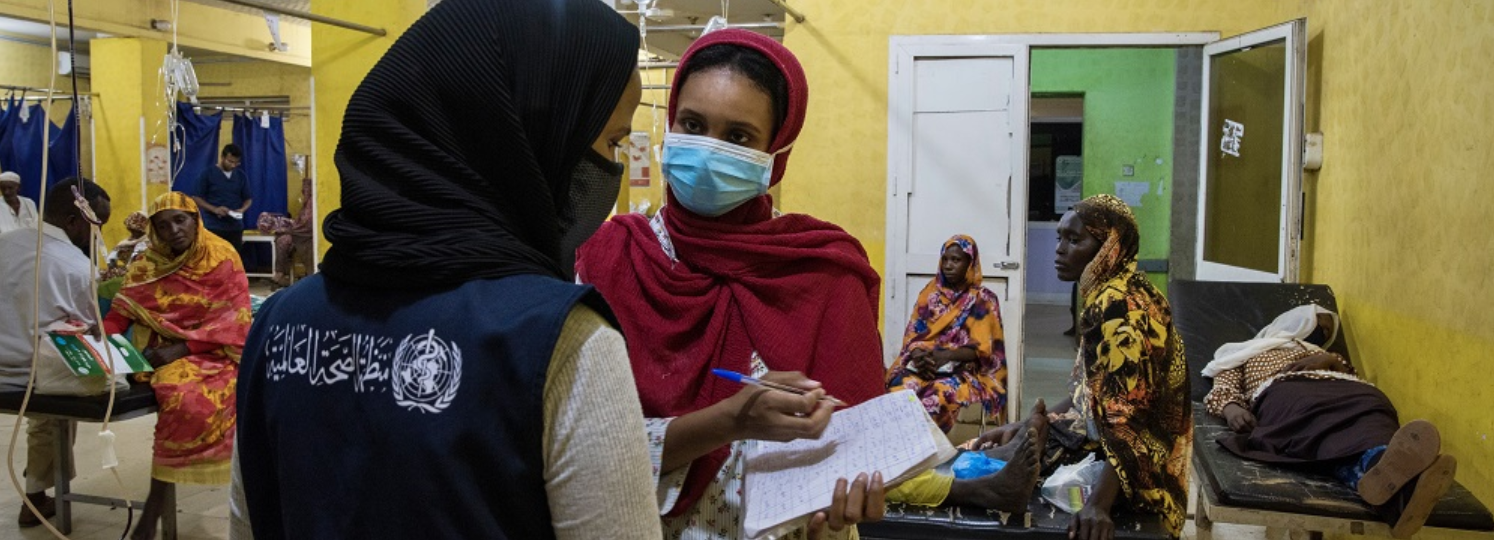
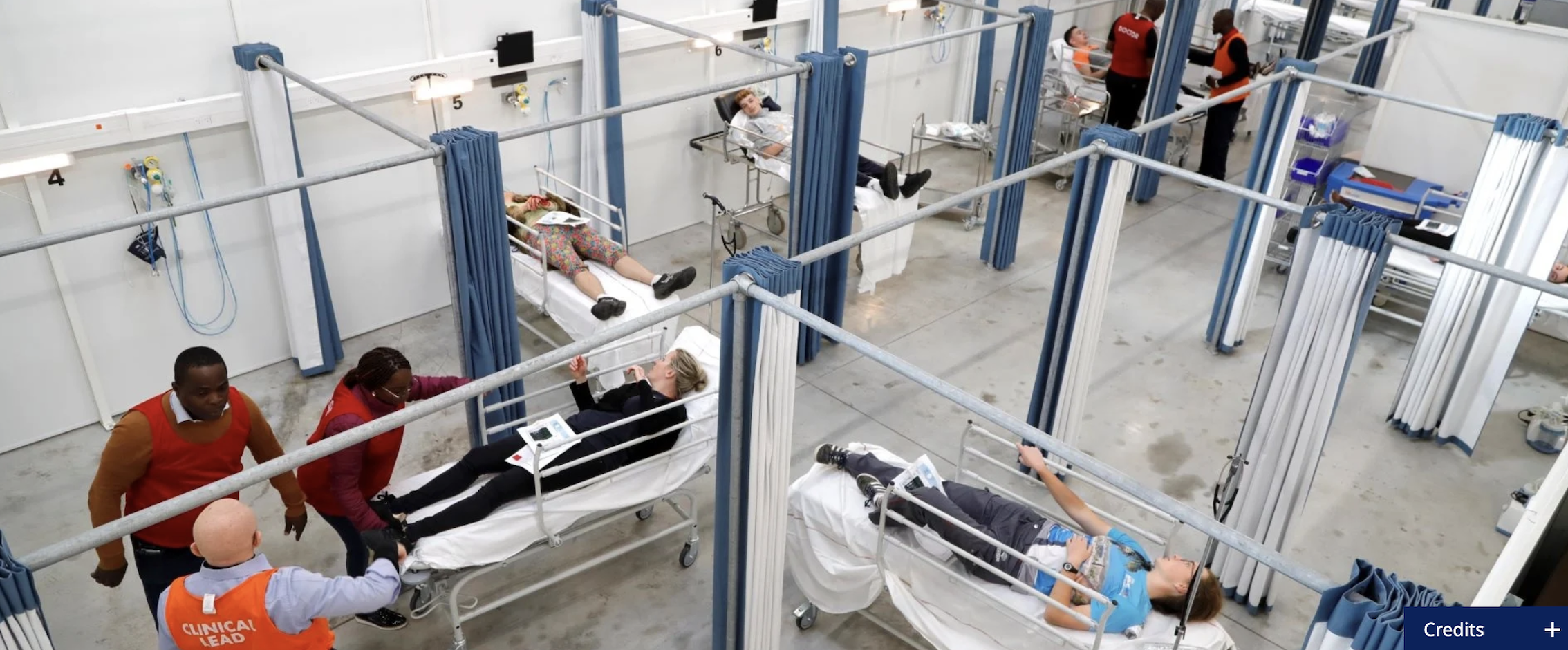
Mass casualty incidents (MCIs) are characterized by a sudden surge in patients that overwhelms the capacity of local medical resources, often resulting in preventable mortality and morbidity. Whether caused by natural disasters, violence, or road traffic crash, MCIs pose significant challenges to clinical service delivery, particularly in resource-limited settings.
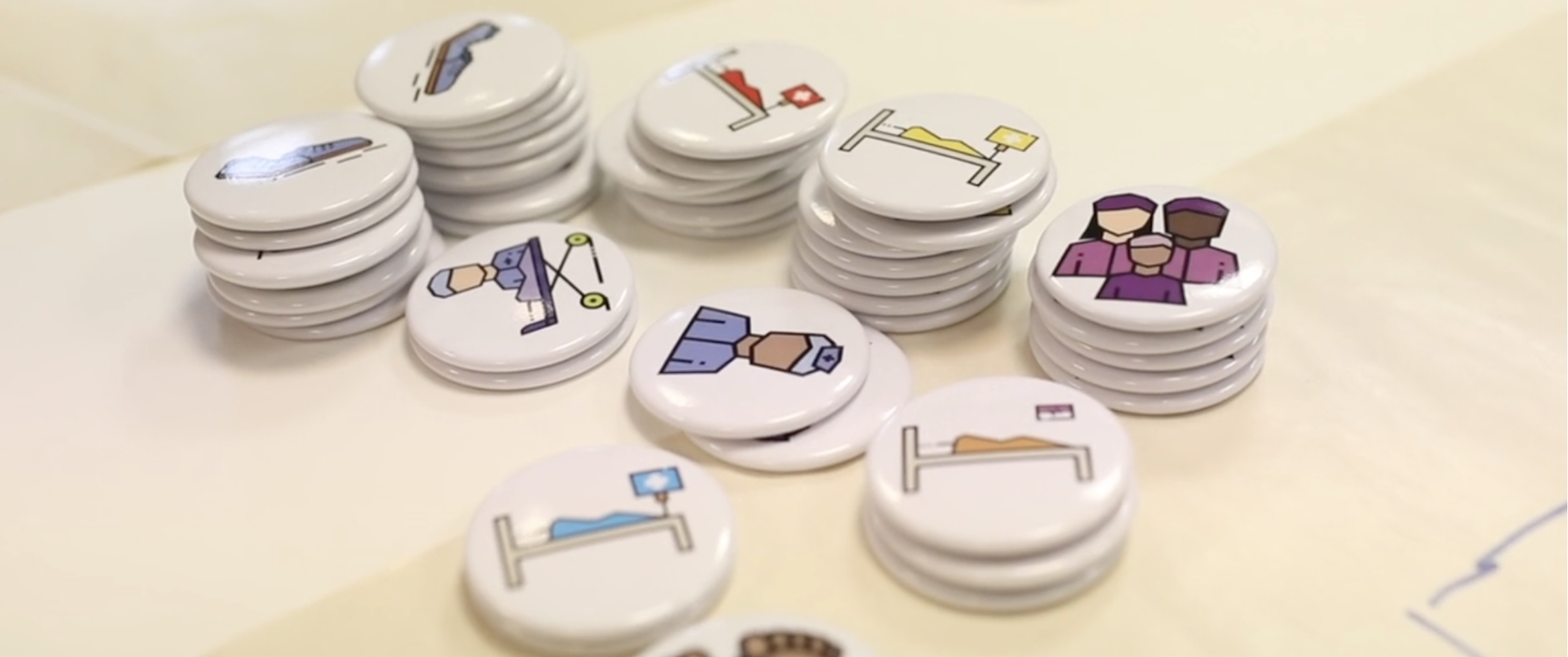
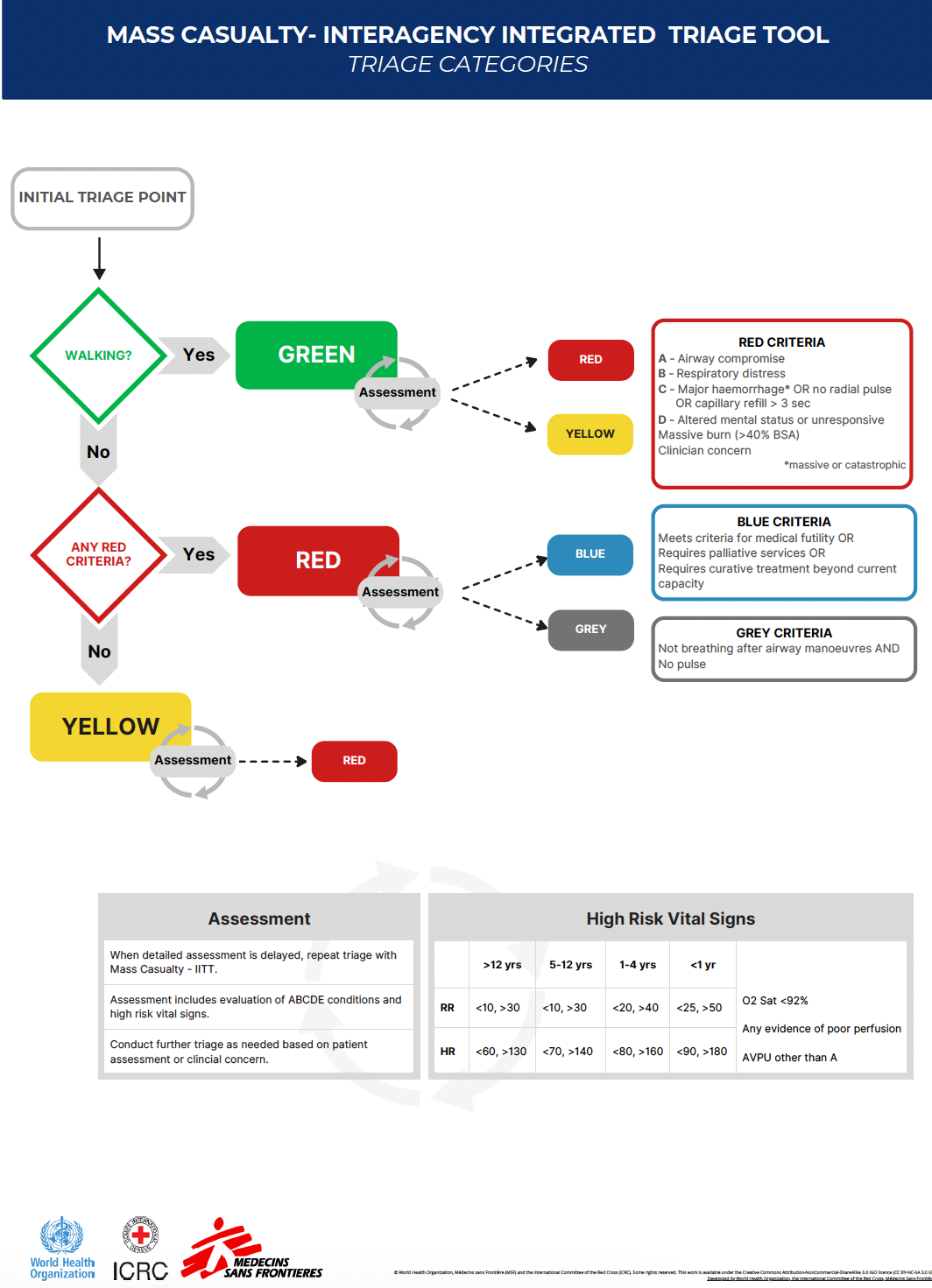
A successful mass casualty response requires a fundamental shift in the approach to patient care. In the day-to-day care of patients, an emergency unit (EU) will aim to ensure the best possible outcome for each patient as an individual. However, in a mass casualty situation, where human and material resources are, by definition, inadequate, it is necessary to identify and provide treatment to those who will most likely benefit from medical intervention. This change in approach is reflected in all the elements of Mass Casualty Management (MCM), from the point of triage to the allocation of resources, and ultimately, the definitive treatment pathway.
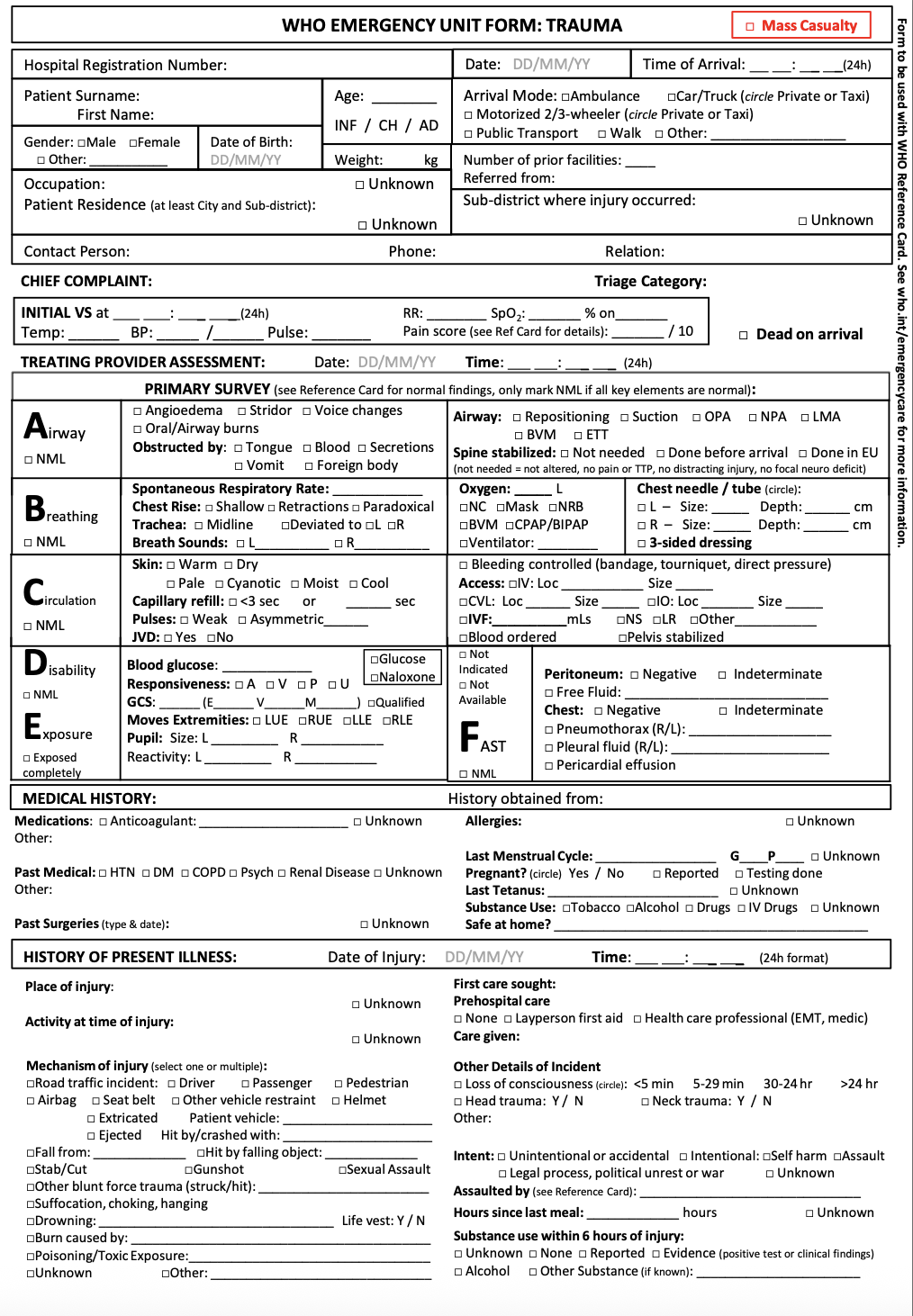
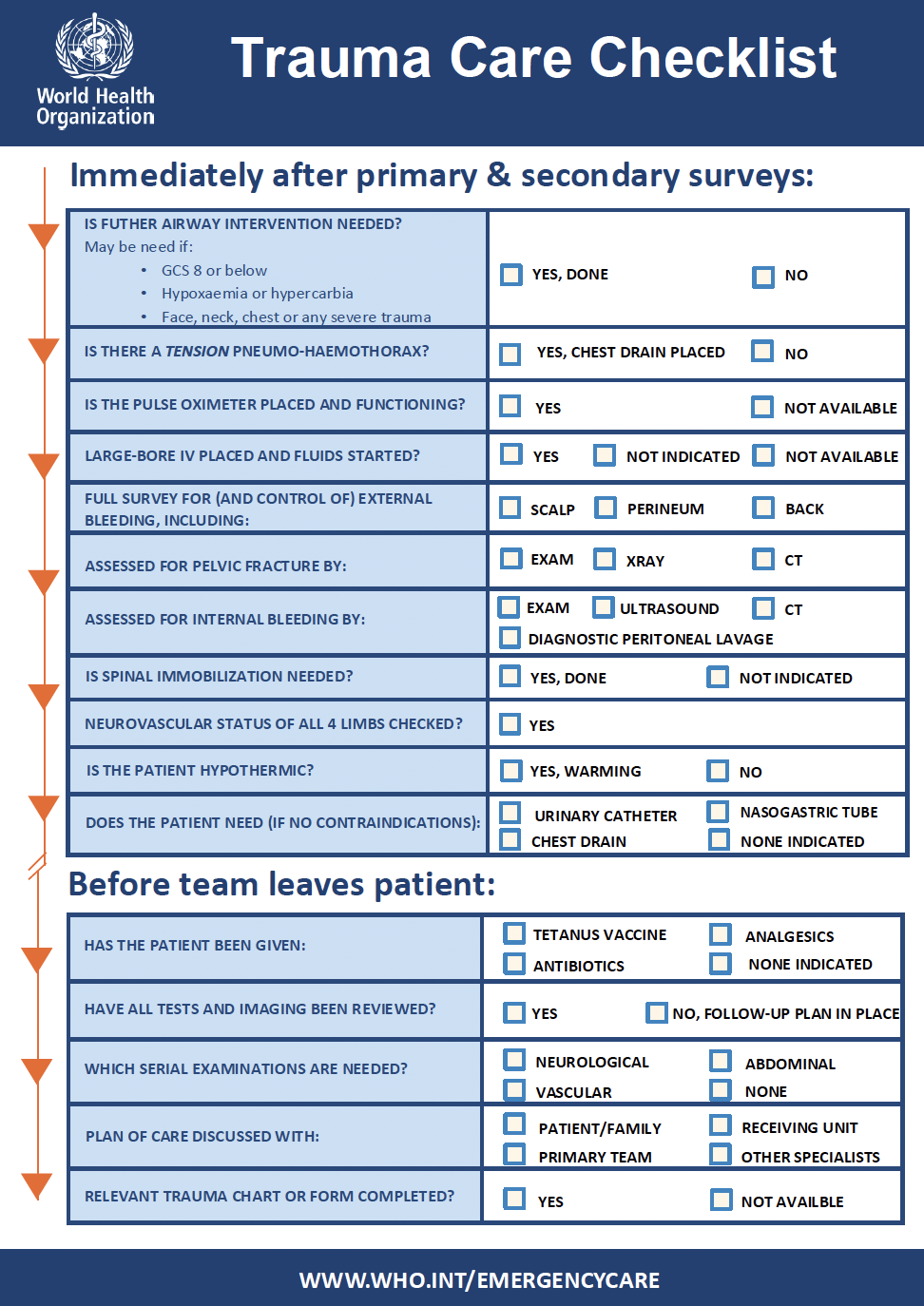
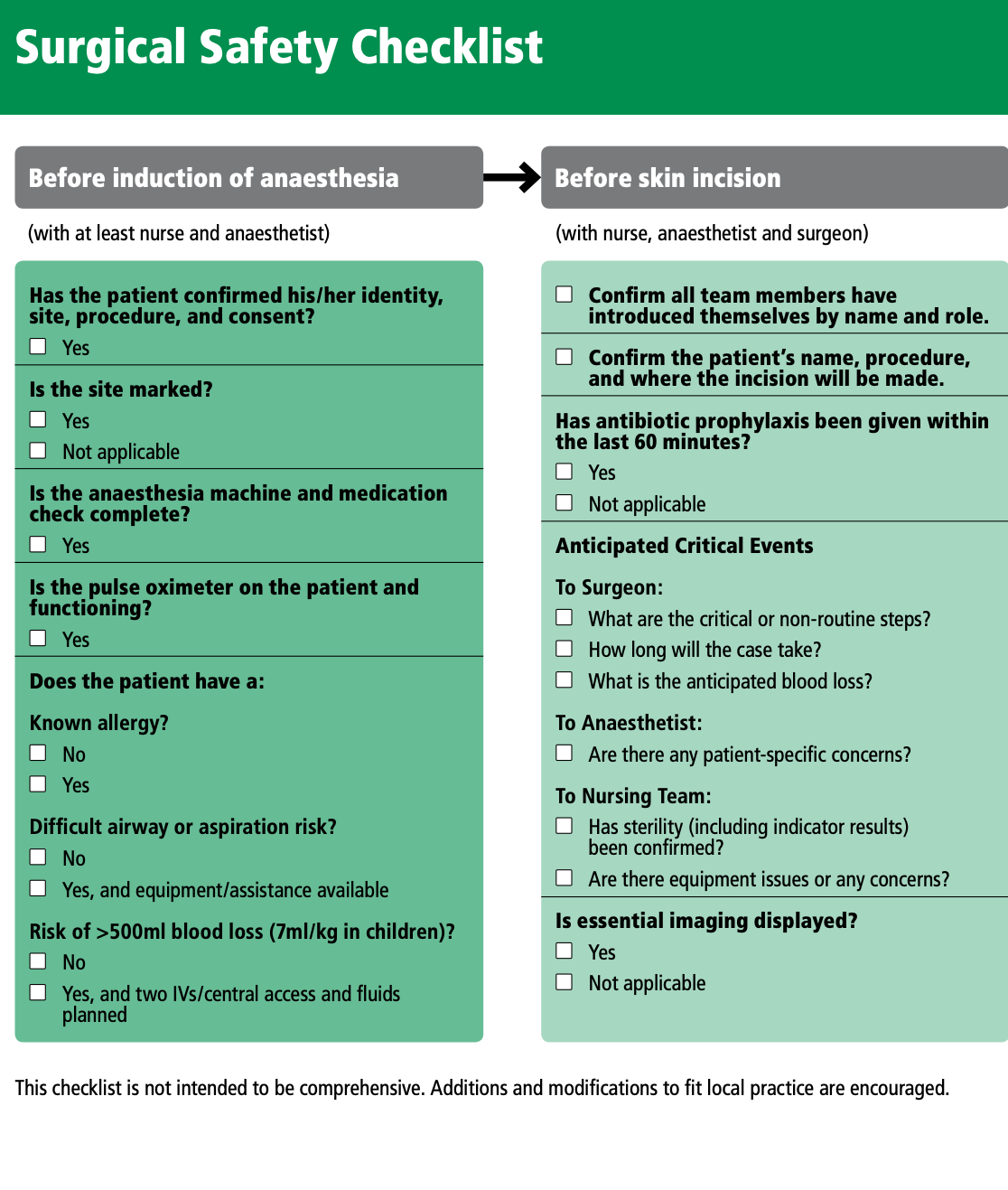
Facility-based EUs play a critical role in managing MCIs, ensuring timely recognition, triage, resuscitation and disposition of patients. In response, WHO has developed comprehensive resources to enhance the ability of healthcare providers and institutions to effectively prepare for, respond to and recover from MCIs. While mass casualty management is most often used during a sudden onset events causing injuries, the principles and tools covered on this page can be applied to any circumstances causing an overwhelming surge of patients, such as during epidemics or exposure to chemical agents.
Media
MCM implementation
Related links
Health topics