Infection prevention and control
Located within the Integrated Health Services (IHS) department, the IPC Unit provides technical leadership and coordination of the infection prevention and control work at WHO headquarters.

Surgical site infection
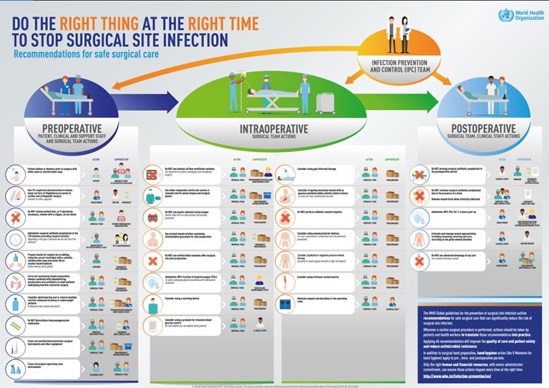
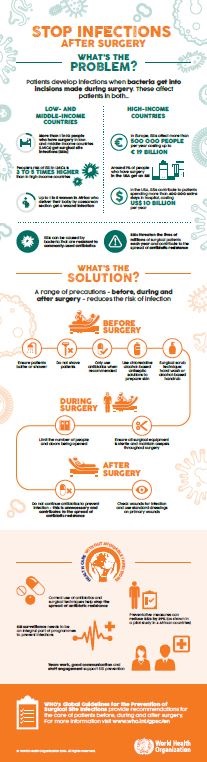
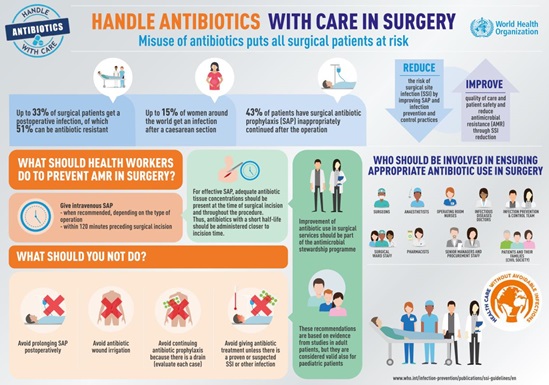
Surgical site infections are caused by bacteria that get in through incisions made during surgery. They threaten the lives of millions of patients each year and contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance. In low- and middle-income countries, 11% of patients who undergo surgery are infected in the process. In Africa, up to 20% of women who have a caesarean section contract a wound infection, compromising their own health and their ability to care for their babies.
But surgical site infections are not just a problem for poor countries. In the United States, they contribute to patients spending more than 400 000 extra days in hospital at an additional cost of US$ 900 million per year.
But surgical site infections are not just a problem for poor countries. In the United States, they contribute to patients spending more than 400 000 extra days in hospital at an additional cost of US$ 900 million per year.
Guidelines

18 November 2022
Decontamination and reprocessing of medical devices for health care facilities: aide-memoire
Decontamination of medical devices plays an important role in the prevention of health care-associated infections. It includes cleaning, disinfection and/or...

1 December 2018
Global guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection
The first ever Global guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection (SSI) were published on 3 November 2016, then updated in some parts and...

Following recent threats caused by widespread epidemics and increasing awareness about the spread of antimicrobial resistance, several countries are paying...
Content related to the global guidelines
Related links
- Lancet Infectious Disease publication: New WHO recommendations on preoperative measures for surgical site infection prevention: an evidence-based global perspective
- Lancet Infectious Disease publication: New WHO recommendations on intraoperative and postoperative measures for surgical site infection prevention: an evidence-based global perspective
- The European Centres for Disease Control (ECDC) have launched their latest report on surgical site infections from 2013-2014 on 3 November 2016 found here.
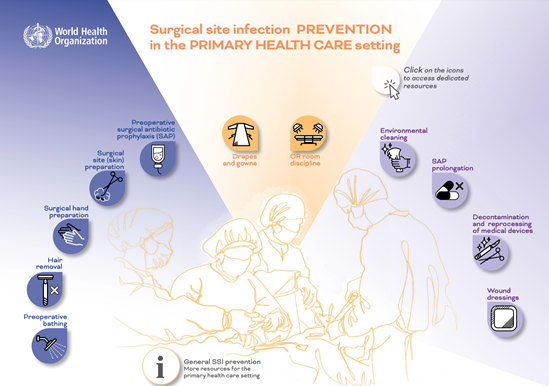
SSI prevention recommendations
Implementation

Interim version
Additional resources
- Modified WHO formulations for surgical hand preparation
- Protocol for evaluation of tolerability and acceptability of alcohol-based handrub in use or planned to be introduced: Method 1
- Protocol for evaluation of tolerability and acceptability of alcohol-based handrub in use or planned to be introduced: Method 2
- Guide to local production: WHO-recommended handrub formulations
- Perioperative staff safety assessment
- Learn from defects tool – Perioperative setting
- Surveys on patient safety culture
- The CUSP method
- WHO Surgical safety checklist 2009
Training
A range of educational tools exist for you to adopt and adapt to support health worker training on the prevention of surgical site infections.