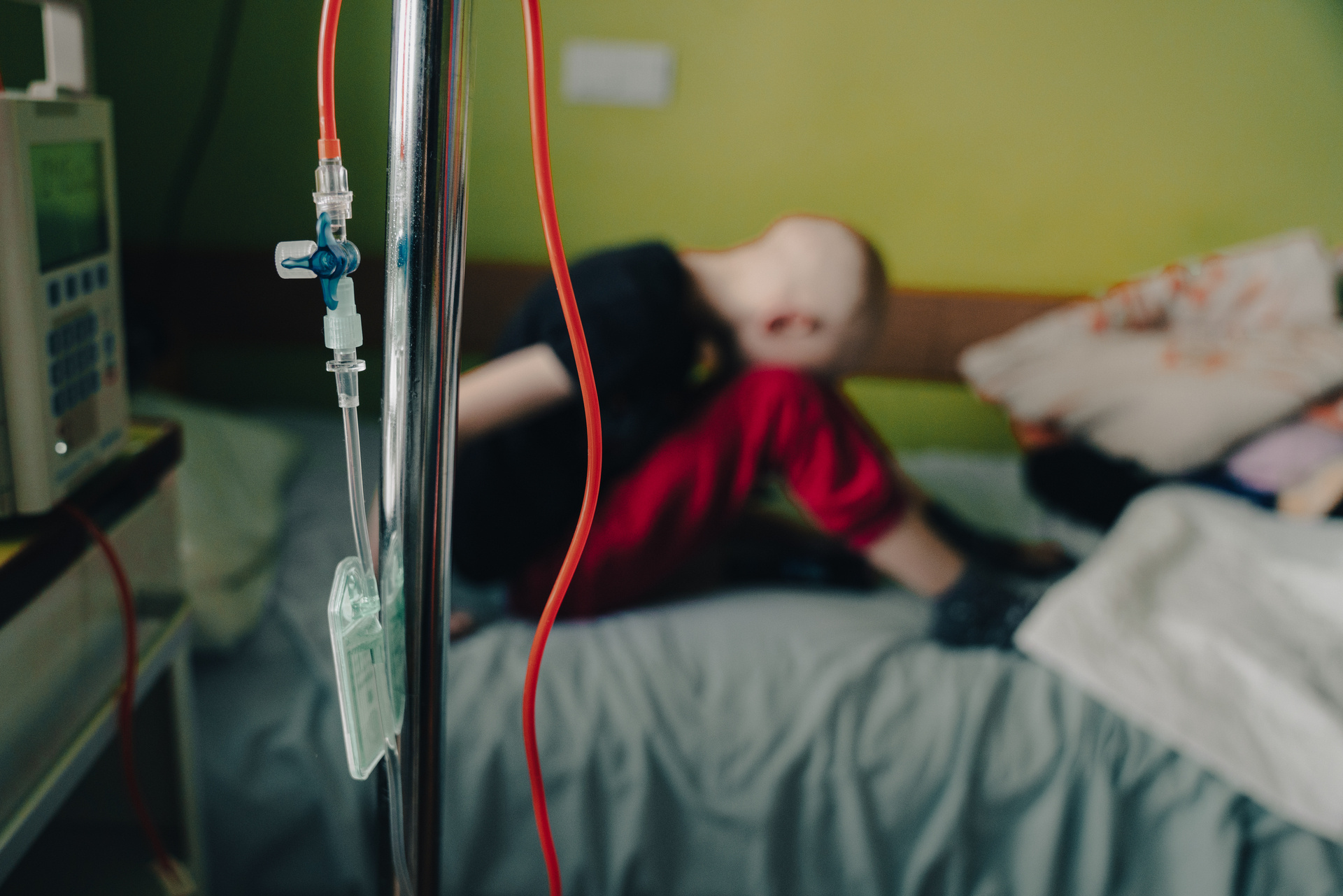
Cancer programme
Cancer is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The majority of the cancer burden occurs in low- and middle-income countries where cancer has a profound social and economic effect on communities because of the limited access to care.
Acting on the World Health Assembly (2017) resolution on cancer prevention and control (WHA70.12), WHO urges Member States to accelerate action towards reducing premature mortality from cancer by developing and reinforcing cancer control programmes. Cancer control includes the systematic implementation of evidence-based interventions for prevention, early detection diagnosis, treatment and palliative care.
Controlling cancer: WHO sets norms and standards for cancer control, and promotes national cancer control policies, plans and programmes.
Ensuring quality treatment: WHO works with governments to strengthen health systems to ensure that cancer patients receive high-quality, affordable, safe and effective medicines, vaccines and diagnostics for cancer.
Preventing cancer: WHO works with Member States to raise awareness and reduce exposure to cancer risk factors, and also ensure that people are provided with the information and support they need to adopt healthy lifestyles.
Promoting cancer early diagnosis: WHO supports Member States to develop and implement cancer early diagnosis and screening programmes to improve cancer outcomes by providing care at the earliest possible stage.
Supporting countries to strengthen palliative care: WHO develops evidence-based guidelines and tools on palliative care, including: pain management options, integration of palliative care into national health systems, and guidance for the availability and accessibility of controlled medicines.
Announcement
News
Our work
Resolutions and decisions
Related fact sheet
Work of the Cancer programme
There is a striking need to address
children's and women’s cancers as a matter of priority and to scale-up
effective diagnosis and treatment. Significant investments involving a broad
range of partners in comprehensive cancer control are required and crucial to
improving the quality of life of vulnerable communities while at the same time
strengthening national health systems. It is against this backdrop that WHO
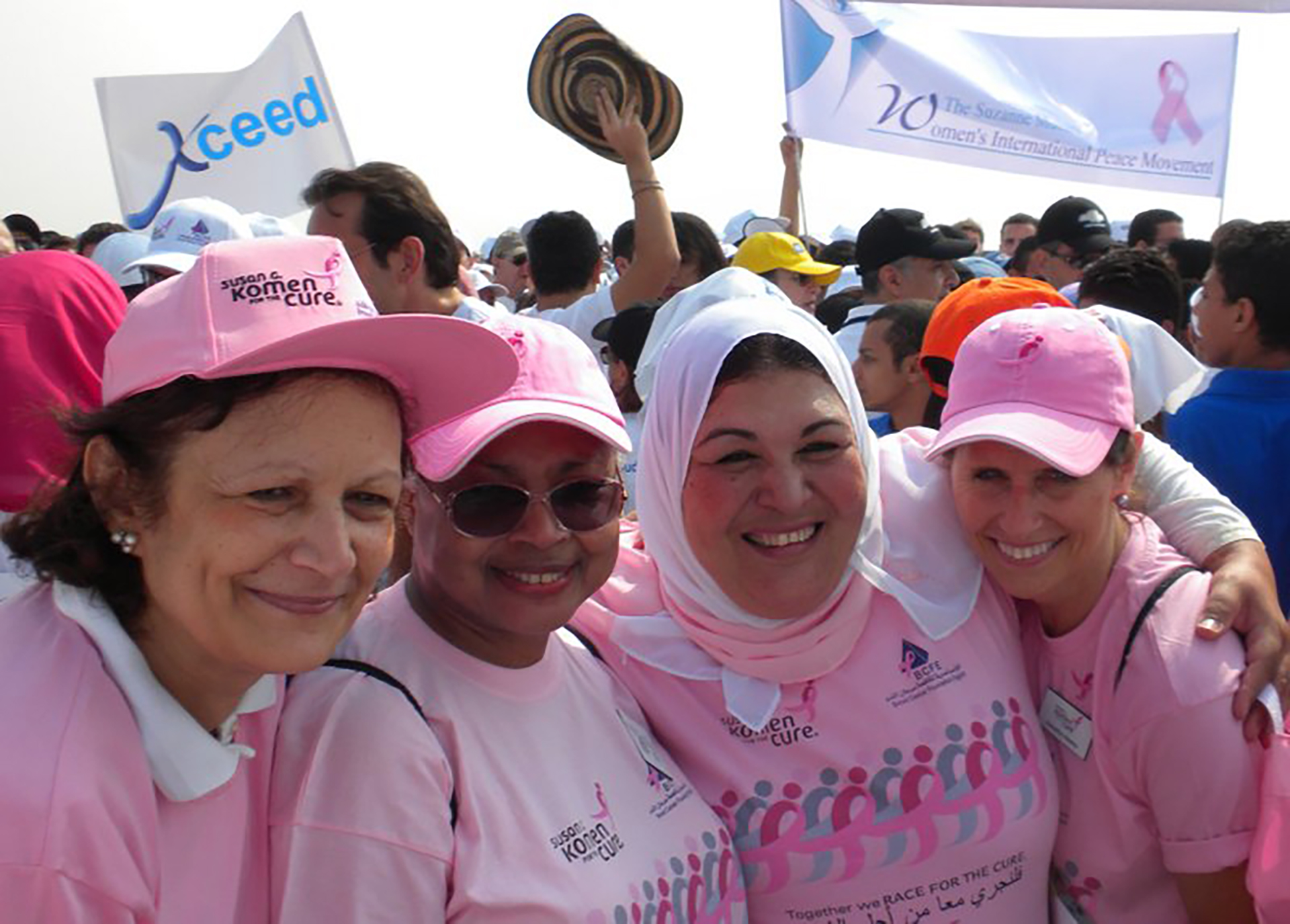
launched 3 integrated cancer initiatives in breast, cervical cancers and childhood now being implemented in more than 75
countries.










.jpeg?sfvrsn=80527ba4_4)

