Strengthening global preparedness to radiation emergencies
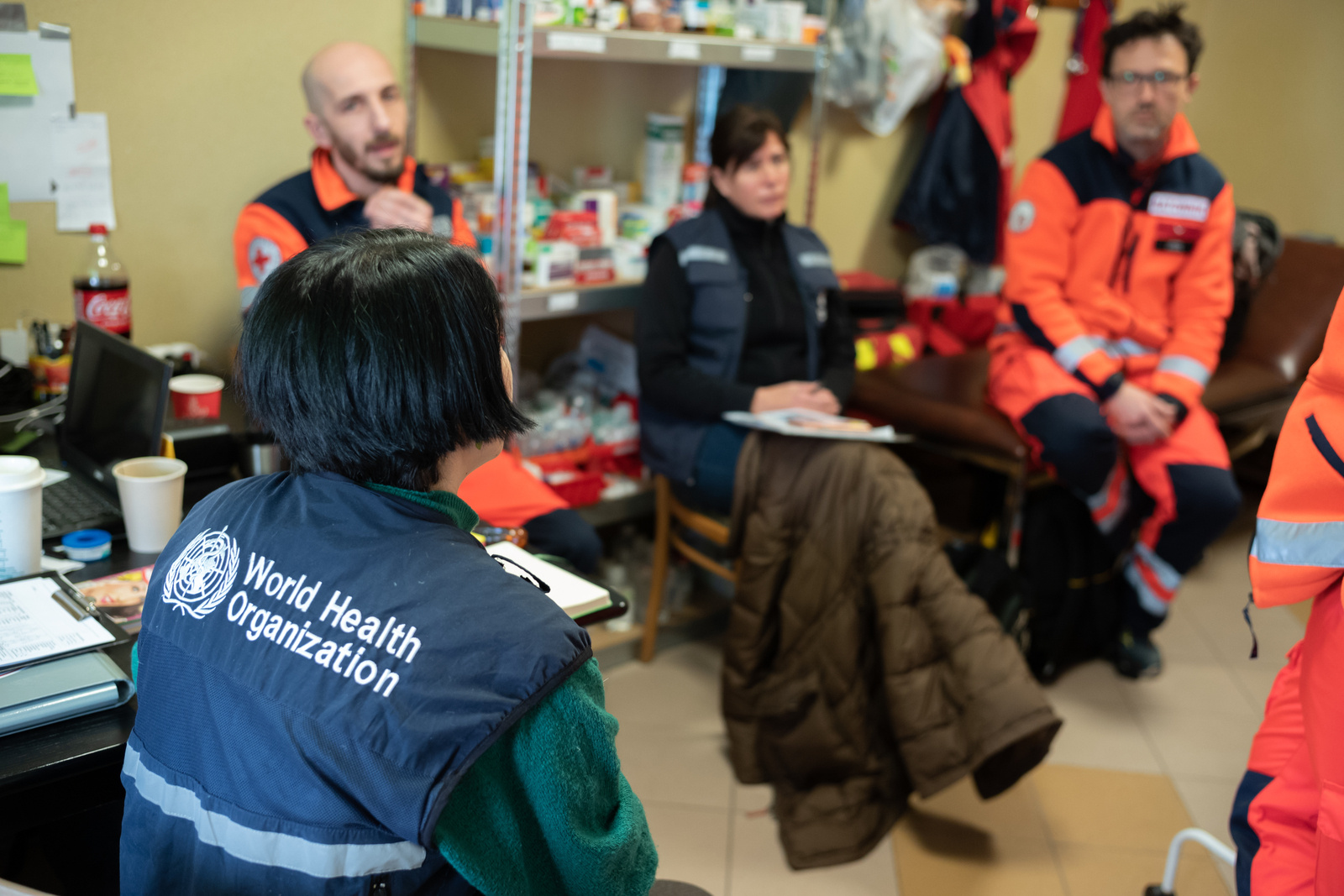
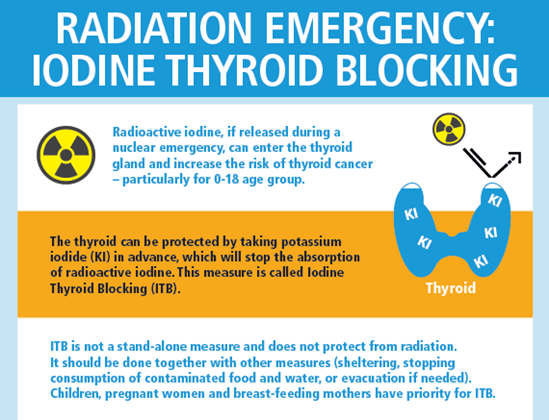
Types of radiological and nuclear emergencies range from an over-exposure of one person to a major emergency with global dimensions. Since 2008, the International Health Regulations (2005) include in their scope radio-nuclear hazards. Countries are expected to meet the core national capacity requirements pertaining to radiation emergencies. Public health sector must be prepared to provide care to the affected persons. WHO uses its Collaborating Centres and global expert networks Radiation Emergency Medical Preparedness and Assistance Network (REMPAN) and BioDoseNet to assist countries to strengthen their national capacities through developing technical guidance and tools, information dissemination, training, exercises, and support to the research and development.
WHO works with other international organizations under the framework of the Inter-agency CommitteeInter-agency Committee for Radiological and nuclear Emergencies (IACRNE) for Radiological and nuclear Emergencies (IACRNE) to provide policy advice and technical support for national health authorities on preparedness, response, recovery and long-term follow-up for populations affected by radiation emergencies.