Creating age-friendly cities and communities
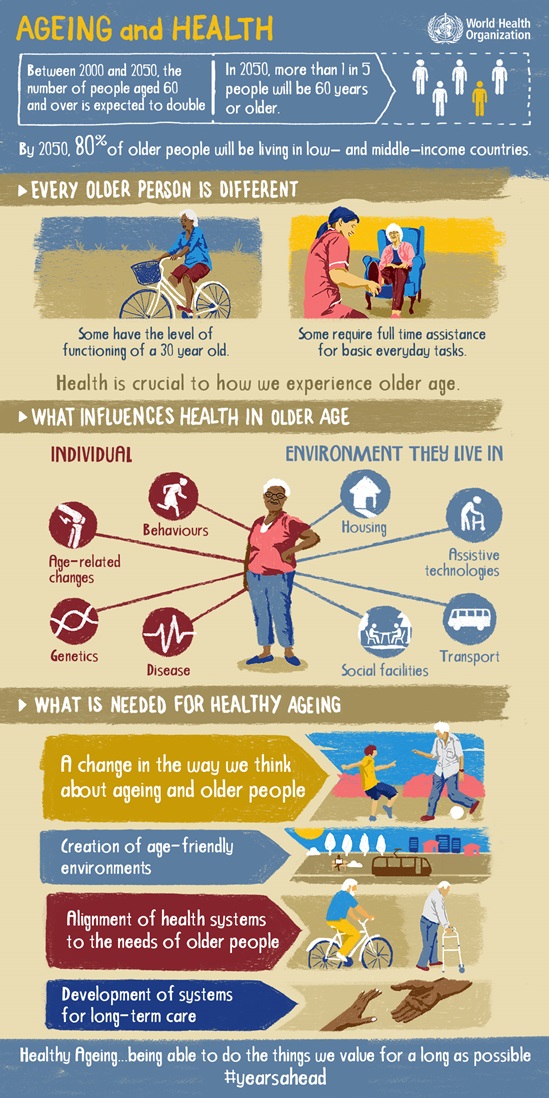
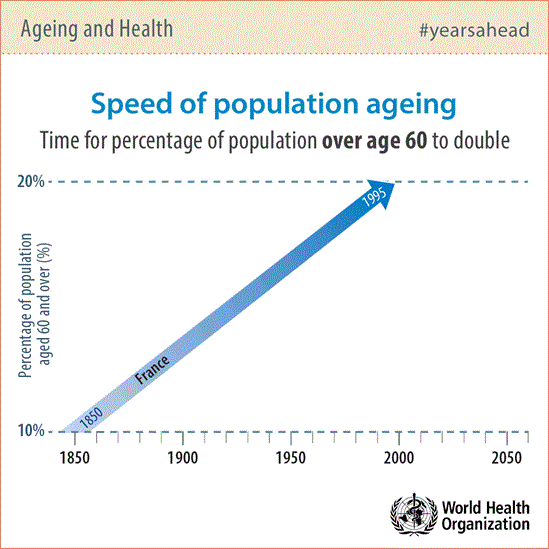
Population ageing and urbanization are two of the biggest social transformations of the 21st century. Cities and communities have a key role in enabling people to live longer and healthier lives while fostering fairer and more sustainable societies.
An age-friendly city or community is health promoting and designed for diversity, inclusion, and cohesion, including across all ages and capacities. Age-friendly cities or communities might have, for example: accessible and safe road and transport infrastructure, barrier-free access to buildings and houses, and public seating and sanitary facilities, among others. Age-friendly cities and communities also enable people to stay active; keep connected; and contribute to their community’s economic, social, and cultural life. An age-friendly city can foster solidarity among generations, facilitating social relationships between residents of all ages. Age-friendly cities and communities also have mechanisms to reach out to older people at risk of social isolation, falls or violence through personalized and tailored efforts.
WHO is working with its Member States at national and local levels to develop age-friendly cities and communities, within the context of the UN Decade of Healthy Ageing (2021-2030). WHO also supports a Global Network for Age-friendly Cities and Communities that works to stimulate and enable cities and communities around the world to become increasingly age-friendly by:
- inspiring change by showing what can be done and how it can be done;
- connecting cities and communities worldwide to facilitate the exchange of information, knowledge and experience; and
- supporting cities and communities to find appropriate innovative and evidence-based solutions.