Strategic Information
The integrated Global Health Sector Strategies on, respectively, HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections for the period 2022-2030 (GHSS) re-affirm the ambitious targets set in 2016 and further define global targets for 2025 and 2030. The GHSS on viral hepatitis calls for elimination of viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030.
Countries should have a national health information system, which can reliably generate and analyse the data necessary to monitor and assess progress against the hepatitis elimination criteria, as well as impact and programme targets.
Strategic information can be defined as data collected at all service delivery and administrative levels to inform policy and programme decisions. In the field of viral hepatitis, strategic information includes surveillance as well as monitoring and evaluation. Surveillance describes the epidemiological situation, from new hepatitis infections to chronic infections and sequelae that lead to morbidity and mortality.
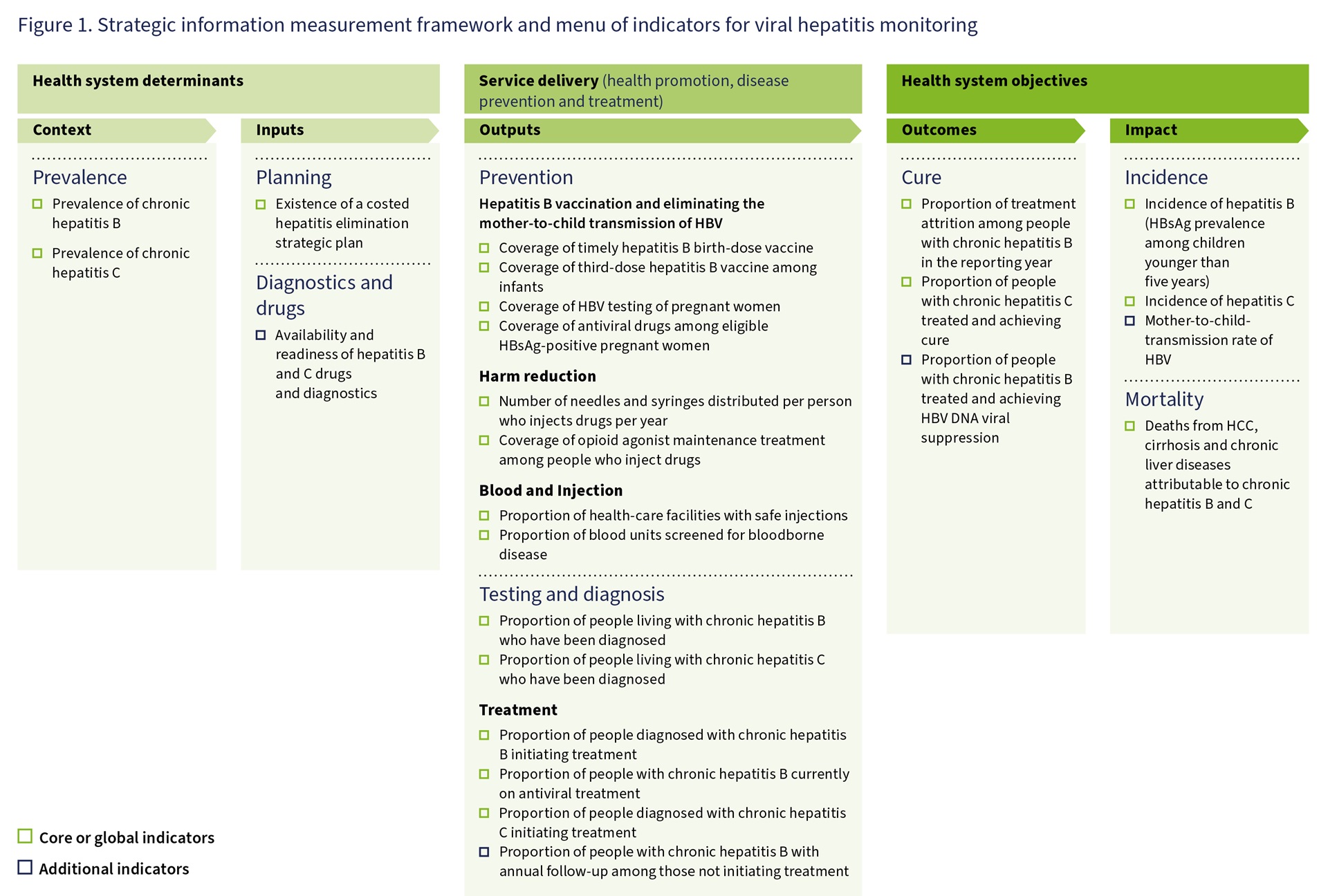
The monitoring and evaluation framework for viral hepatitis tracks how hepatitis programmes are performing using a standard results-based approach that considers context (prevalence of infection), measures input, output and outcomes (including the cascade of prevention, testing and treatment), and impact (incidence and mortality). These components contribute to a comprehensive picture of the epidemiological situation of viral hepatitis. They provide strategic information to inform policy and programme decisions, and to monitor progress towards the elimination of viral hepatitis as a public health threat.
The data systems required to inform this framework include:
- surveillance for acute hepatitis A–E chronic infections (mostly B and C), and sequelae (caused by decompensated liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer);
- programme data documenting prevention, testing and treatment, including the cascade of care; and
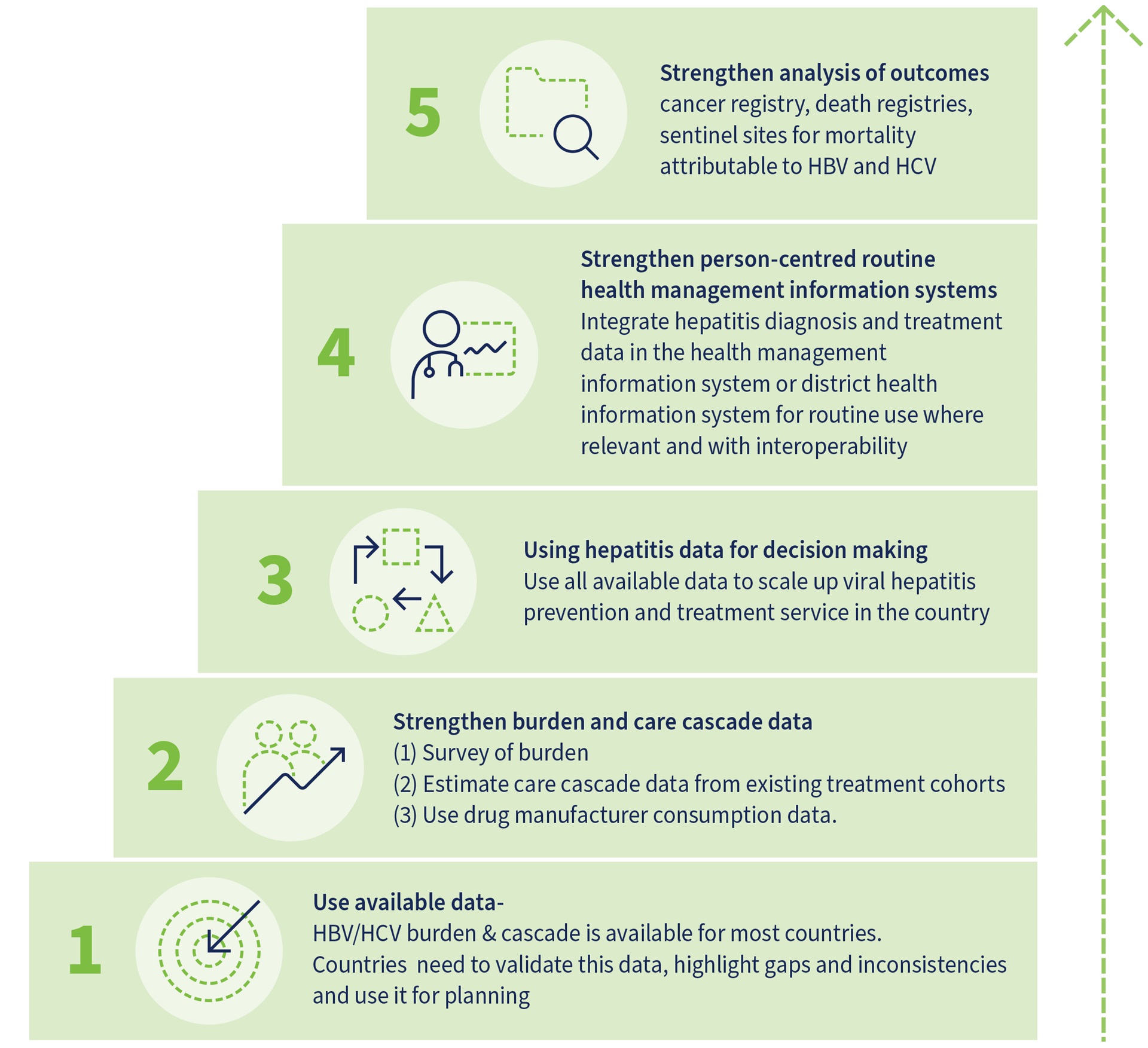
- A stepwise approach is recommended for implementing surveillance for viral hepatitis, using the data available while strengthening the data system. In the first phase, a survey is needed to generate estimates for the epidemiology as well as the natural history of hepatitis in the country. In the second phase, person-centred routine programme data are needed to manage and monitor viral hepatitis testing and treatment coverage.


Strategic information measurement framework and menu of indicators for viral hepatitis monitoring
Core indicators for viral hepatitis B and C monitoring
A stepwise recommendation for strengthening country surveillance of viral hepatitis
Data and statistics on hepatitis
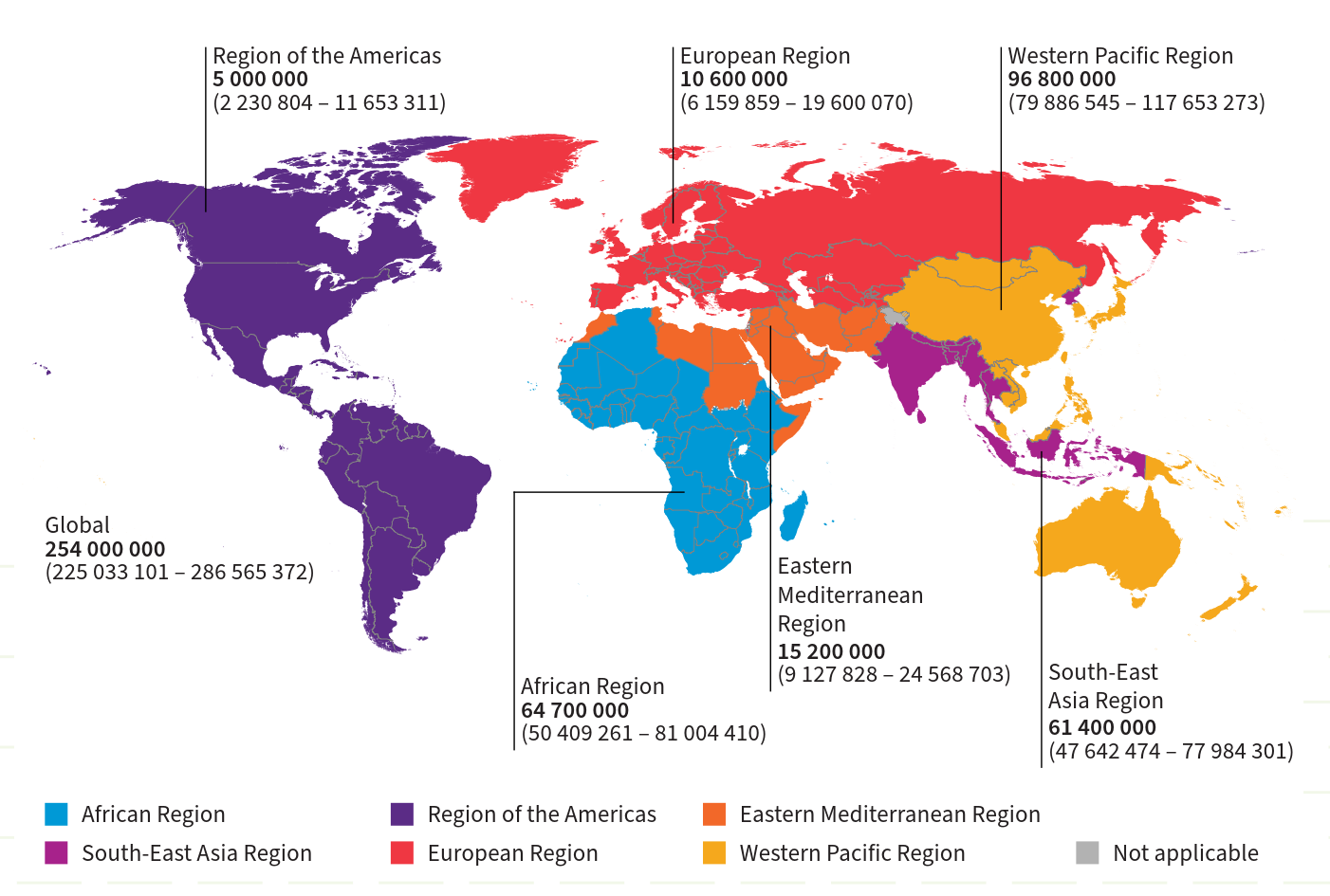
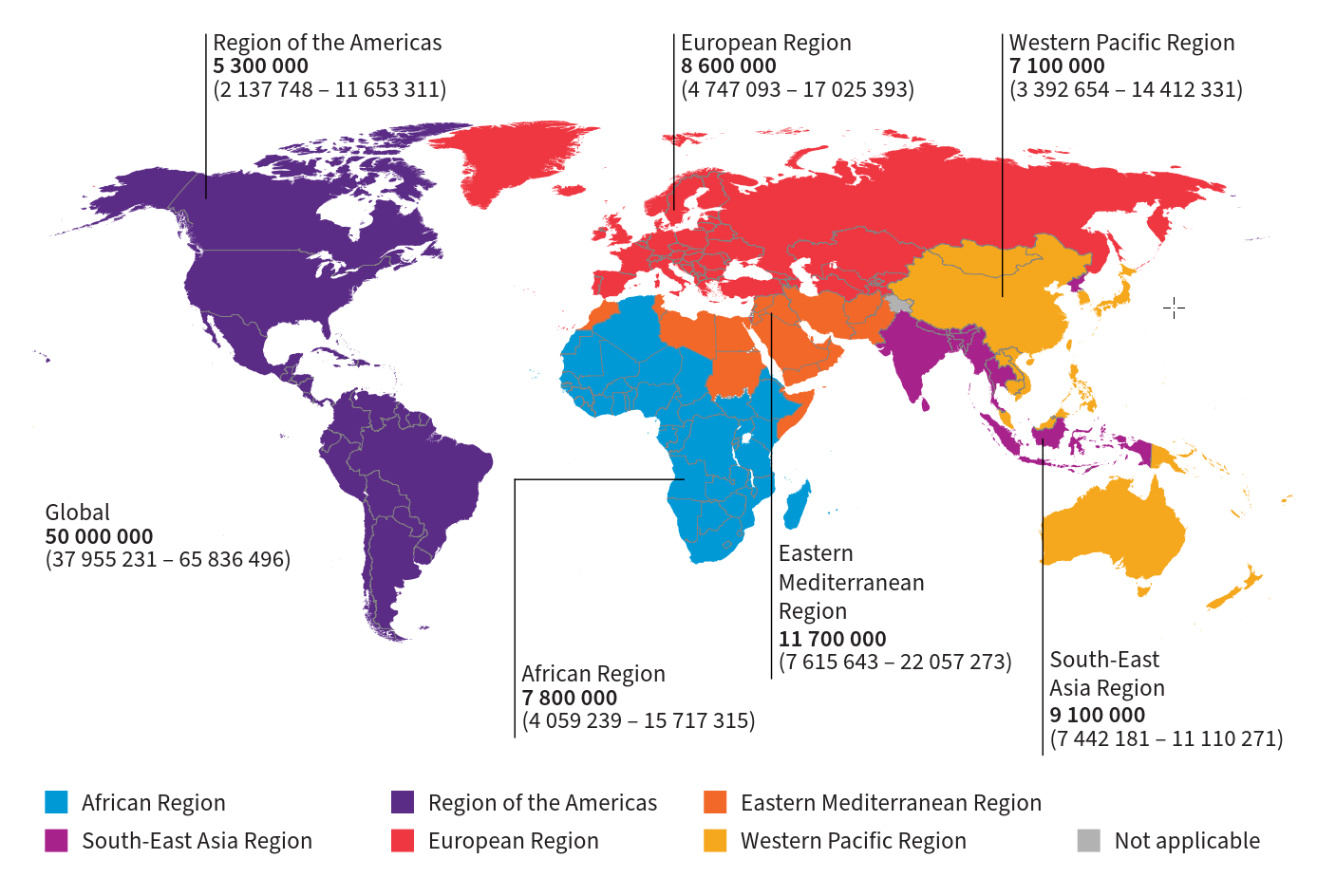
Prevalent cases of chronic hepatitis B and C, 2022
Guidelines
All →
Consolidated guidelines on person-centred viral hepatitis...
Publications and technical reports

This is the first consolidated WHO report on viral hepatitis epidemiology, service coverage and product access, with improved data for action. This report...

Guidance for country validation of viral hepatitis elimination and path to elimination
Building on the 2021 Interim guidance, this second version and update, incorporates the lessons and feedback from the hepatitis pilots that successfully...

Criteria for validation of elimination of viral hepatitis B and C: report of 7 country pilots
A series of country pilots (Brazil, Egypt, Georgia, Mongolia, Rwanda, Thailand and United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland) of the elimination...

Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021
This report provides accountability for the 3 Global Health Sector Strategies (2016-2021) on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and the STIs. The report assesses the...

WHO implementation tool for monitoring the toxicity of new antiretroviral and antiviral medicines in...
In the current context of treatment being rapidly scaled up, prolonged exposure to ARV drugs and transition to new antiretroviral (ARV) drugs, ARV toxicity...

Technical considerations and case definitions to improve surveillance for viral hepatitis - policy brief
In 2010 and 2014, World Health Assembly resolutions called for stronger surveillance of viral hepatitis. In response, the World Health Organization has...

Monitoring and evaluation for viral hepatitis B and C: recommended indicators and framework
To monitor and evaluate the Global Health Sector Strategy (GHSS) on viral hepatitis, the World Health Organization (WHO) proposes a monitoring and evaluation...
Journal articles
Worldwide prevalence of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus among patients with cirrhosis at country, region, and global levels: a systematic review - The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, August 2022
Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040 - Journal of Hepatology August 2022
Progress Toward the Elimination of Mother-to-Child Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus - Worldwide, 2016-2021- MMWR Morbidity Mortality Weekly Report July 2022
Methods and indicators to validate country reductions in incidence of hepatitis C virus infection to elimination levels set by WHO - The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, April 2022
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and incidence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in men who have sex with men (MSM) - The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 17 November 2020
The global prevalence of hepatitis D virus infection: systematic review and meta-analysis - Journal of Hepatology, April 2020
Injection practices in 2011–2015: a review using data from the demographic and health surveys (DHS) - BMC Health Services Research, August 2019
Prevalence and burden of HBV co-infection among people living with HIV: A global systematic review and meta-analysis - Journal of Viral Hepatitis, October 2019
Prevalence and burden of HCV co-infection in people living with HIV: a global systematic review and meta-analysis - The Lancet Infectious Diseases, February 2016