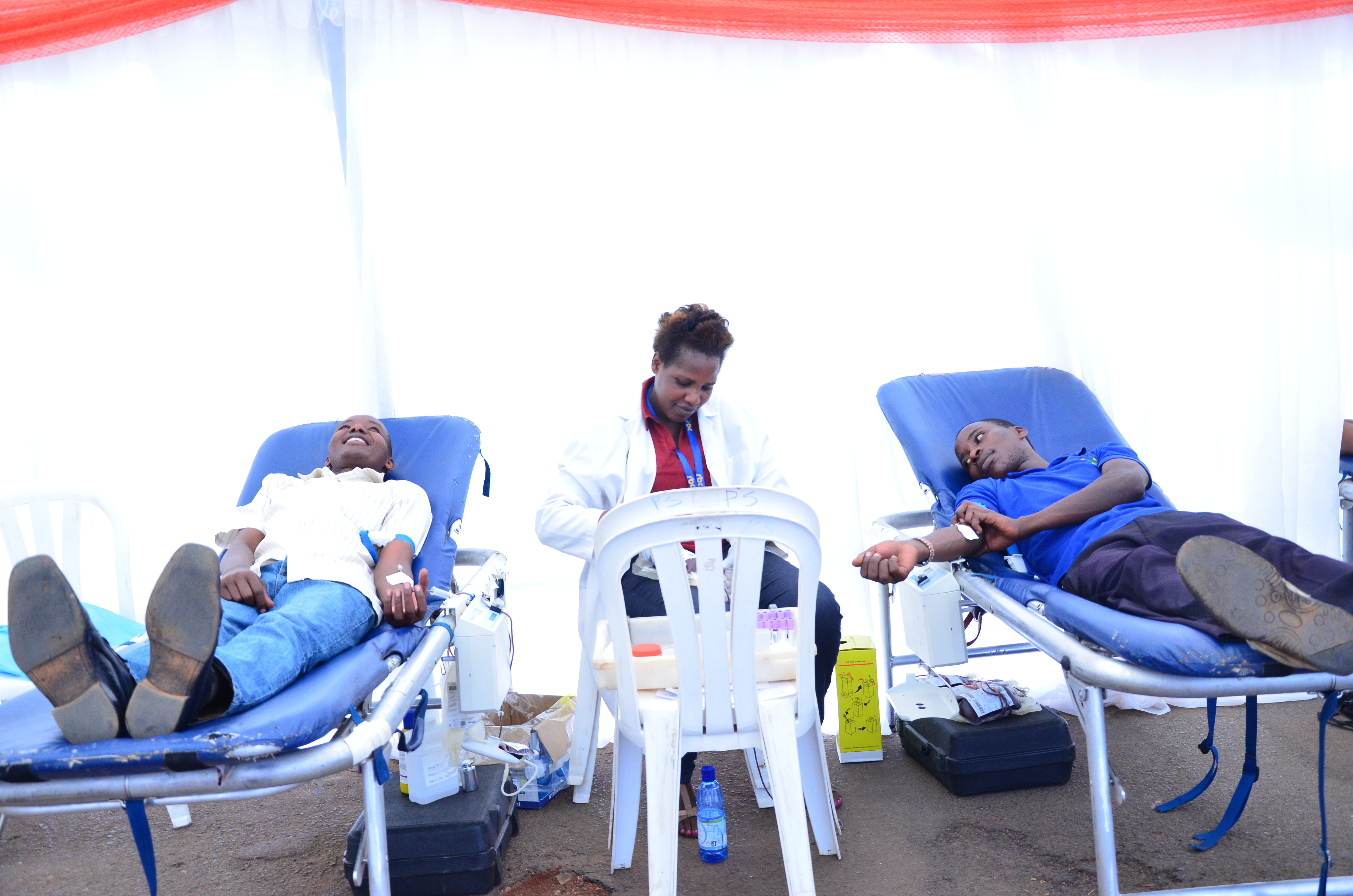
Quality and Safety of blood products
Biological medicines such as blood products and related in vitro diagnostic tests are life-saving components of every day medical practice worldwide. Although scientific evidence shows that blood products have never been safer since the introduction of several measures in the last years, uncertainty still persists in the public perception of how safe blood components and plasma products are. Particular safety considerations arise from the biological nature of the starting materials used, the manufacturing process involved and the test methods needed to characterize the production consistency.
Harmonization on quality assurance and safety of blood products calls for a quality assurance system based on the existence of a national structure that is independent of the manufacturer and that is responsible for granting licenses for blood products, defining procedures for products release and for post-marketing surveillance systems.
In order to avoid transmission of infectious agents, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) should be adopted as an essential tool of the quality assurance system. In addition, GMP should be adhered to at all levels of the manufacturing process, from the collection of the source materials to the quality control of the final product, thus ensuring traceability from the donor to the recipient.
The provision of plasma products requires the availability of sufficient plasma of assured quality and safety. Policies for mandatory testing should be determined by the national control authority, and should be reviewed regularly and modified according to the current state of knowledge. Blood/plasma donor selection, collection procedures, testing methods, donation handling, storage and transport of plasma should follow defined quality assurance procedures, the importance of which has been highlighted by international guidelines. Improved single donation and plasma pool testing as well as improved manufacturing methods for purification and virus inactivation have enhanced the safety of blood components and plasma derivatives.
It is a WHO priority to contribute to the advancement of technical expertise of National Regulatory Authorities and the formation of regulatory regional networks so that only blood products of assured quality and safety are used worldwide.
Technical and Regulatory Assistance to National Regulatory Authorities
WHO Workshops (webit)
Focus areas
WHO publications

Action framework to advance universal access to safe, effective and quality-assured blood products 2020–2023
In response to calls for action, WHO has provided guidelines, physical standards, training and technical support to improve blood product quality, safety...

Establishing external quality assessment programmes for screening of donated blood for transfusion-transmissible...
Establishing external quality assessment programmes for screening of donated blood for transfusion-transmissible infections: implementation guide aims...

External quality assessment of transfusion laboratory practice: guidelines on establishing an EQA Scheme...
Blood transfusion is an essential and life-saving support within the health care system, yet the safety of transfusion is not assured globally, particularly...

Blood transfusion is a key part of modern health care. It is the responsibility of the national blood programme to provide an adequate supply of blood...
Meeting reports