Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) for Infectious Diseases
Passive immunization for post-exposure prophylaxis or adjunct therapy has been successfully used for over a century to treat suspected exposure or infection against a range of diseases, such as rabies, diphtheria, tetanus, and hepatitis B. For most of these diseases, the immunoglobulin preparations administered to patients have been derived from immunized horses, immunized humans, and in some cases from convalescent patients. However, these products have presented several challenges including standardization of production, safety, supply and access, which has led many groups to explore replacing these products with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).
In addition to potentially addressing the production, safety and supply limitations of blood-derived immunoglobulins, anti-infective mAbs may offer, for some infectious diseases, prophylactic or therapeutic interventions where effective treatments are not available or where vaccines remain elusive. Furthermore, anti-infective mAbs could be used to target multi-drug resistant pathogens, and may also contribute to reduced rates of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Although protection is short-lived, passive immunization with monoclonal antibodies has some advantages over active immunization with vaccines:
- Protection afforded via passive immunization is immediate, and such protection can be induced in immunosuppressed individuals who are often at the highest risk of infection;
- Since the process for manufacturing is generic, a facility can in principal switch on production of a monoclonal antibody with minimal lead time, enabling rapid availability of a product in an outbreak; and
- New technologies such as extending the half-life of the antibody or injecting mRNA coding for a monoclonal antibody, may simplify the production or administration of monoclonal antibodies.
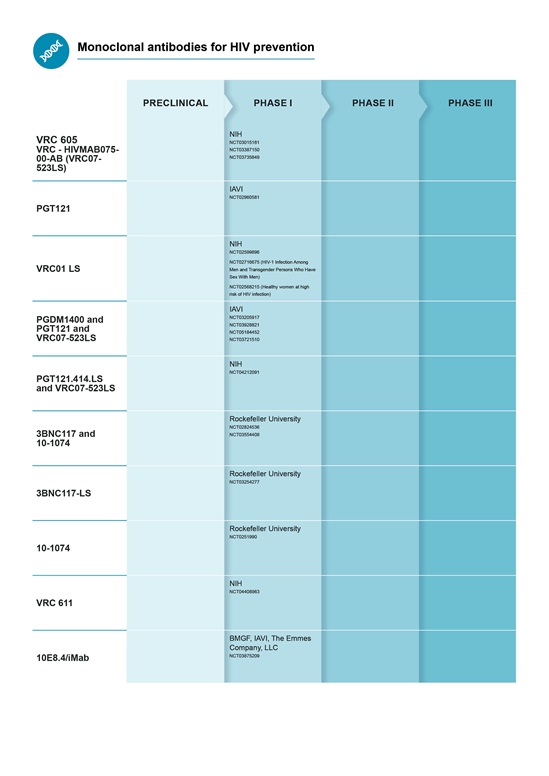
PDR has ongoing activities related to HIV, malaria, rabies and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) mAbs.
Preferred Product Characteristics (PPCs) monoclonal antibodies for RSV,HIV and malaria have been published.

Monoclonal antibodies for malaria prevention
Preferred product characteristics (PPCs) are key tools to incentivize and guide the development of urgently needed health products. The PPCs published...

It is a priority for WHO to ensure that products are developed in a manner that supports optimal use globally, including in low- and middle-income countries...
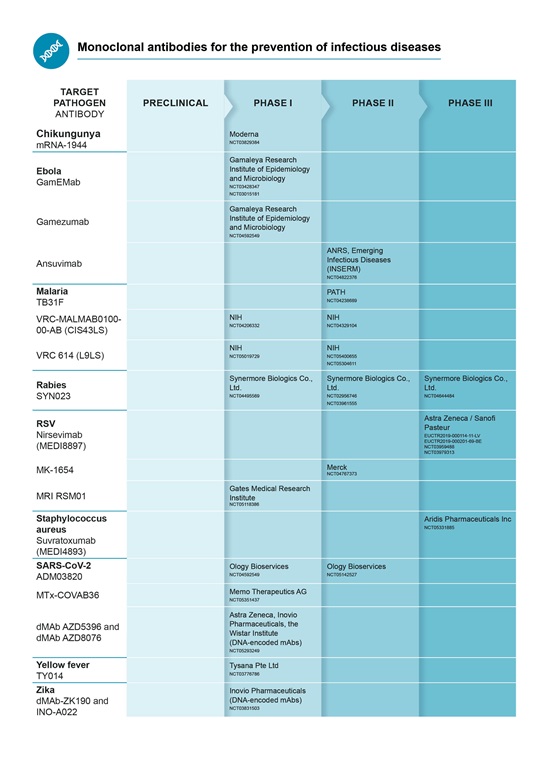
Pipeline for mAbs for infectious disease prevention
Related publications

Recent advances in the development of monoclonal antibodies for rabies post exposure prophylaxis: A review...
Despite successful control in many parts of the world, rabies virus continues to result in tens of thousands of deaths each year. Death from rabies can...

Passive immunization for influenza through antibody therapies, a review of the pipeline, challenges and...
The Global Action Plan for influenza vaccines (GAP) aims to increase the production capacity of vaccines so that in the event of a pandemic there is an...

Therapeutic antibodies for infectious diseases
Passive immunization has been used in the global effort to eliminate maternal and neonatal tetanus. Researchers have estimated that vaccinating pregnant...